- About MogDB
- Quick Start
- MogDB Playground
- Container-based MogDB Installation
- Installation on a Single Node
- MogDB Access
- Use CLI to Access MogDB
- Use GUI to Access MogDB
- Use Middleware to Access MogDB
- Use Programming Language to Access MogDB
- Using Sample Dataset Mogila
- Characteristic Description
- High Performance
- High Availability (HA)
- Maintainability
- Database Security
- Access Control Model
- Separation of Control and Access Permissions
- Database Encryption Authentication
- Data Encryption and Storage
- Database Audit
- Network Communication Security
- Resource Label
- Unified Audit
- Dynamic Data Anonymization
- Row-Level Access Control
- Password Strength Verification
- Equality Query in a Fully-encrypted Database
- Ledger Database Mechanism
- Enterprise-Level Features
- Support for Functions and Stored Procedures
- SQL Hints
- Full-Text Indexing
- Copy Interface for Error Tolerance
- Partitioning
- Support for Advanced Analysis Functions
- Materialized View
- HyperLogLog
- Creating an Index Online
- Autonomous Transaction
- Global Temporary Table
- Pseudocolumn ROWNUM
- Stored Procedure Debugging
- JDBC Client Load Balancing and Read/Write Isolation
- In-place Update Storage Engine
- Application Development Interfaces
- AI Capabilities
- Installation Guide
- Container Installation
- Simplified Installation Process
- Standard Installation
- Manual Installation
- Administrator Guide
- Routine Maintenance
- Starting and Stopping MogDB
- Using the gsql Client for Connection
- Routine Maintenance
- Checking OS Parameters
- Checking MogDB Health Status
- Checking Database Performance
- Checking and Deleting Logs
- Checking Time Consistency
- Checking The Number of Application Connections
- Routinely Maintaining Tables
- Routinely Recreating an Index
- Data Security Maintenance Suggestions
- Log Reference
- Primary and Standby Management
- MOT Engine
- Introducing MOT
- Using MOT
- Concepts of MOT
- Appendix
- Column-store Tables Management
- Backup and Restoration
- Importing and Exporting Data
- Importing Data
- Exporting Data
- Upgrade Guide
- Routine Maintenance
- AI Features Guide
- Overview
- Predictor: AI Query Time Forecasting
- X-Tuner: Parameter Optimization and Diagnosis
- SQLdiag: Slow SQL Discovery
- A-Detection: Status Monitoring
- Index-advisor: Index Recommendation
- DeepSQL
- AI-Native Database (DB4AI)
- Security Guide
- Developer Guide
- Application Development Guide
- Development Specifications
- Development Based on JDBC
- Overview
- JDBC Package, Driver Class, and Environment Class
- Development Process
- Loading the Driver
- Connecting to a Database
- Connecting to the Database (Using SSL)
- Running SQL Statements
- Processing Data in a Result Set
- Closing a Connection
- Managing Logs
- Example: Common Operations
- Example: Retrying SQL Queries for Applications
- Example: Importing and Exporting Data Through Local Files
- Example 2: Migrating Data from a MY Database to MogDB
- Example: Logic Replication Code
- Example: Parameters for Connecting to the Database in Different Scenarios
- JDBC API Reference
- java.sql.Connection
- java.sql.CallableStatement
- java.sql.DatabaseMetaData
- java.sql.Driver
- java.sql.PreparedStatement
- java.sql.ResultSet
- java.sql.ResultSetMetaData
- java.sql.Statement
- javax.sql.ConnectionPoolDataSource
- javax.sql.DataSource
- javax.sql.PooledConnection
- javax.naming.Context
- javax.naming.spi.InitialContextFactory
- CopyManager
- Development Based on ODBC
- Development Based on libpq
- Development Based on libpq
- libpq API Reference
- Database Connection Control Functions
- Database Statement Execution Functions
- Functions for Asynchronous Command Processing
- Functions for Canceling Queries in Progress
- Example
- Connection Characters
- Psycopg-Based Development
- Commissioning
- Appendices
- Stored Procedure
- User Defined Functions
- PL/pgSQL-SQL Procedural Language
- Scheduled Jobs
- Autonomous Transaction
- Logical Replication
- Logical Decoding
- Foreign Data Wrapper
- Materialized View
- Materialized View Overview
- Full Materialized View
- Incremental Materialized View
- Resource Load Management
- Overview
- Resource Management Preparation
- Application Development Guide
- Performance Tuning Guide
- System Optimization
- SQL Optimization
- WDR Snapshot Schema
- TPCC Performance Tuning Guide
- Reference Guide
- System Catalogs and System Views
- Overview of System Catalogs and System Views
- System Catalogs
- GS_AUDITING_POLICY
- GS_AUDITING_POLICY_ACCESS
- GS_AUDITING_POLICY_FILTERS
- GS_AUDITING_POLICY_PRIVILEGES
- GS_CLIENT_GLOBAL_KEYS
- GS_CLIENT_GLOBAL_KEYS_ARGS
- GS_COLUMN_KEYS
- GS_COLUMN_KEYS_ARGS
- GS_ENCRYPTED_COLUMNS
- GS_ENCRYPTED_PROC
- GS_GLOBAL_CHAIN
- GS_MASKING_POLICY
- GS_MASKING_POLICY_ACTIONS
- GS_MASKING_POLICY_FILTERS
- GS_MATVIEW
- GS_MATVIEW_DEPENDENCY
- GS_OPT_MODEL
- GS_POLICY_LABEL
- GS_RECYCLEBIN
- GS_TXN_SNAPSHOT
- GS_WLM_INSTANCE_HISTORY
- GS_WLM_OPERATOR_INFO
- GS_WLM_PLAN_ENCODING_TABLE
- GS_WLM_PLAN_OPERATOR_INFO
- GS_WLM_EC_OPERATOR_INFO
- PG_AGGREGATE
- PG_AM
- PG_AMOP
- PG_AMPROC
- PG_APP_WORKLOADGROUP_MAPPING
- PG_ATTRDEF
- PG_ATTRIBUTE
- PG_AUTHID
- PG_AUTH_HISTORY
- PG_AUTH_MEMBERS
- PG_CAST
- PG_CLASS
- PG_COLLATION
- PG_CONSTRAINT
- PG_CONVERSION
- PG_DATABASE
- PG_DB_ROLE_SETTING
- PG_DEFAULT_ACL
- PG_DEPEND
- PG_DESCRIPTION
- PG_DIRECTORY
- PG_ENUM
- PG_EXTENSION
- PG_EXTENSION_DATA_SOURCE
- PG_FOREIGN_DATA_WRAPPER
- PG_FOREIGN_SERVER
- PG_FOREIGN_TABLE
- PG_INDEX
- PG_INHERITS
- PG_JOB
- PG_JOB_PROC
- PG_LANGUAGE
- PG_LARGEOBJECT
- PG_LARGEOBJECT_METADATA
- PG_NAMESPACE
- PG_OBJECT
- PG_OPCLASS
- PG_OPERATOR
- PG_OPFAMILY
- PG_PARTITION
- PG_PLTEMPLATE
- PG_PROC
- PG_RANGE
- PG_RESOURCE_POOL
- PG_REWRITE
- PG_RLSPOLICY
- PG_SECLABEL
- PG_SHDEPEND
- PG_SHDESCRIPTION
- PG_SHSECLABEL
- PG_STATISTIC
- PG_STATISTIC_EXT
- PG_SYNONYM
- PG_TABLESPACE
- PG_TRIGGER
- PG_TS_CONFIG
- PG_TS_CONFIG_MAP
- PG_TS_DICT
- PG_TS_PARSER
- PG_TS_TEMPLATE
- PG_TYPE
- PG_USER_MAPPING
- PG_USER_STATUS
- PG_WORKLOAD_GROUP
- PLAN_TABLE_DATA
- STATEMENT_HISTORY
- System Views
- GET_GLOBAL_PREPARED_XACTS
- GS_AUDITING
- GS_AUDITING_ACCESS
- GS_AUDITING_PRIVILEGE
- GS_CLUSTER_RESOURCE_INFO
- GS_INSTANCE_TIME
- GS_LABELS
- GS_MASKING
- GS_MATVIEWS
- GS_SESSION_MEMORY
- GS_SESSION_CPU_STATISTICS
- GS_SESSION_MEMORY_CONTEXT
- GS_SESSION_MEMORY_DETAIL
- GS_SESSION_MEMORY_STATISTICS
- GS_SQL_COUNT
- GS_WLM_CGROUP_INFO
- GS_WLM_PLAN_OPERATOR_HISTORY
- GS_WLM_REBUILD_USER_RESOURCE_POOL
- GS_WLM_RESOURCE_POOL
- GS_WLM_USER_INFO
- GS_STAT_SESSION_CU
- GS_TOTAL_MEMORY_DETAIL
- MPP_TABLES
- PG_AVAILABLE_EXTENSION_VERSIONS
- PG_AVAILABLE_EXTENSIONS
- PG_COMM_DELAY
- PG_COMM_RECV_STREAM
- PG_COMM_SEND_STREAM
- PG_COMM_STATUS
- PG_CONTROL_GROUP_CONFIG
- PG_CURSORS
- PG_EXT_STATS
- PG_GET_INVALID_BACKENDS
- PG_GET_SENDERS_CATCHUP_TIME
- PG_GROUP
- PG_GTT_RELSTATS
- PG_GTT_STATS
- PG_GTT_ATTACHED_PIDS
- PG_INDEXES
- PG_LOCKS
- PG_NODE_ENV
- PG_OS_THREADS
- PG_PREPARED_STATEMENTS
- PG_PREPARED_XACTS
- PG_REPLICATION_SLOTS
- PG_RLSPOLICIES
- PG_ROLES
- PG_RULES
- PG_SECLABELS
- PG_SETTINGS
- PG_SHADOW
- PG_STATS
- PG_STAT_ACTIVITY
- PG_STAT_ALL_INDEXES
- PG_STAT_ALL_TABLES
- PG_STAT_BAD_BLOCK
- PG_STAT_BGWRITER
- PG_STAT_DATABASE
- PG_STAT_DATABASE_CONFLICTS
- PG_STAT_USER_FUNCTIONS
- PG_STAT_USER_INDEXES
- PG_STAT_USER_TABLES
- PG_STAT_REPLICATION
- PG_STAT_SYS_INDEXES
- PG_STAT_SYS_TABLES
- PG_STAT_XACT_ALL_TABLES
- PG_STAT_XACT_SYS_TABLES
- PG_STAT_XACT_USER_FUNCTIONS
- PG_STAT_XACT_USER_TABLES
- PG_STATIO_ALL_INDEXES
- PG_STATIO_ALL_SEQUENCES
- PG_STATIO_ALL_TABLES
- PG_STATIO_SYS_INDEXES
- PG_STATIO_SYS_SEQUENCES
- PG_STATIO_SYS_TABLES
- PG_STATIO_USER_INDEXES
- PG_STATIO_USER_SEQUENCES
- PG_STATIO_USER_TABLES
- PG_TABLES
- PG_TDE_INFO
- PG_THREAD_WAIT_STATUS
- PG_TIMEZONE_ABBREVS
- PG_TIMEZONE_NAMES
- PG_TOTAL_MEMORY_DETAIL
- PG_TOTAL_USER_RESOURCE_INFO
- PG_TOTAL_USER_RESOURCE_INFO_OID
- PG_USER
- PG_USER_MAPPINGS
- PG_VARIABLE_INFO
- PG_VIEWS
- PLAN_TABLE
- GS_FILE_STAT
- GS_OS_RUN_INFO
- GS_REDO_STAT
- GS_SESSION_STAT
- GS_SESSION_TIME
- GS_THREAD_MEMORY_CONTEXT
- Functions and Operators
- Logical Operators
- Comparison Operators
- Character Processing Functions and Operators
- Binary String Functions and Operators
- Bit String Functions and Operators
- Mode Matching Operators
- Mathematical Functions and Operators
- Date and Time Processing Functions and Operators
- Type Conversion Functions
- Geometric Functions and Operators
- Network Address Functions and Operators
- Text Search Functions and Operators
- JSON/JSONB Functions and Operators
- HLL Functions and Operators
- SEQUENCE Functions
- Array Functions and Operators
- Range Functions and Operators
- Aggregate Functions
- Window Functions
- Security Functions
- Ledger Database Functions
- Encrypted Equality Functions
- Set Returning Functions
- Conditional Expression Functions
- System Information Functions
- System Administration Functions
- Configuration Settings Functions
- Universal File Access Functions
- Server Signal Functions
- Backup and Restoration Control Functions
- Snapshot Synchronization Functions
- Database Object Functions
- Advisory Lock Functions
- Logical Replication Functions
- Segment-Page Storage Functions
- Other Functions
- Undo System Functions
- Statistics Information Functions
- Trigger Functions
- Hash Function
- Prompt Message Function
- Global Temporary Table Functions
- Fault Injection System Function
- AI Feature Functions
- Dynamic Data Masking Functions
- Other System Functions
- Internal Functions
- Obsolete Functions
- Supported Data Types
- Numeric Types
- Monetary Types
- Boolean Types
- Enumerated Types
- Character Types
- Binary Types
- Date/Time Types
- Geometric
- Network Address Types
- Bit String Types
- Text Search Types
- UUID
- JSON/JSONB Types
- HLL
- Array Types
- Range
- OID Types
- Pseudo-Types
- Data Types Supported by Column-store Tables
- XML Types
- Data Type Used by the Ledger Database
- SQL Syntax
- ABORT
- ALTER AGGREGATE
- ALTER AUDIT POLICY
- ALTER DATABASE
- ALTER DATA SOURCE
- ALTER DEFAULT PRIVILEGES
- ALTER DIRECTORY
- ALTER EXTENSION
- ALTER FOREIGN TABLE
- ALTER FUNCTION
- ALTER GROUP
- ALTER INDEX
- ALTER LANGUAGE
- ALTER LARGE OBJECT
- ALTER MASKING POLICY
- ALTER MATERIALIZED VIEW
- ALTER OPERATOR
- ALTER RESOURCE LABEL
- ALTER RESOURCE POOL
- ALTER ROLE
- ALTER ROW LEVEL SECURITY POLICY
- ALTER RULE
- ALTER SCHEMA
- ALTER SEQUENCE
- ALTER SERVER
- ALTER SESSION
- ALTER SYNONYM
- ALTER SYSTEM KILL SESSION
- ALTER SYSTEM SET
- ALTER TABLE
- ALTER TABLE PARTITION
- ALTER TABLE SUBPARTITION
- ALTER TABLESPACE
- ALTER TEXT SEARCH CONFIGURATION
- ALTER TEXT SEARCH DICTIONARY
- ALTER TRIGGER
- ALTER TYPE
- ALTER USER
- ALTER USER MAPPING
- ALTER VIEW
- ANALYZE | ANALYSE
- BEGIN
- CALL
- CHECKPOINT
- CLEAN CONNECTION
- CLOSE
- CLUSTER
- COMMENT
- COMMIT | END
- COMMIT PREPARED
- CONNECT BY
- COPY
- CREATE AGGREGATE
- CREATE AUDIT POLICY
- CREATE CAST
- CREATE CLIENT MASTER KEY
- CREATE COLUMN ENCRYPTION KEY
- CREATE DATABASE
- CREATE DATA SOURCE
- CREATE DIRECTORY
- CREATE EXTENSION
- CREATE FOREIGN TABLE
- CREATE FUNCTION
- CREATE GROUP
- CREATE INCREMENTAL MATERIALIZED VIEW
- CREATE INDEX
- CREATE LANGUAGE
- CREATE MASKING POLICY
- CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW
- CREATE MODEL
- CREATE OPERATOR
- CREATE PACKAGE
- CREATE ROW LEVEL SECURITY POLICY
- CREATE PROCEDURE
- CREATE RESOURCE LABEL
- CREATE RESOURCE POOL
- CREATE ROLE
- CREATE RULE
- CREATE SCHEMA
- CREATE SEQUENCE
- CREATE SERVER
- CREATE SYNONYM
- CREATE TABLE
- CREATE TABLE AS
- CREATE TABLE PARTITION
- CREATE TABLE SUBPARTITION
- CREATE TABLESPACE
- CREATE TEXT SEARCH CONFIGURATION
- CREATE TEXT SEARCH DICTIONARY
- CREATE TRIGGER
- CREATE TYPE
- CREATE USER
- CREATE USER MAPPING
- CREATE VIEW
- CREATE WEAK PASSWORD DICTIONARY
- CURSOR
- DEALLOCATE
- DECLARE
- DELETE
- DO
- DROP AGGREGATE
- DROP AUDIT POLICY
- DROP CAST
- DROP CLIENT MASTER KEY
- DROP COLUMN ENCRYPTION KEY
- DROP DATABASE
- DROP DATA SOURCE
- DROP DIRECTORY
- DROP EXTENSION
- DROP FOREIGN TABLE
- DROP FUNCTION
- DROP GROUP
- DROP INDEX
- DROP LANGUAGE
- DROP MASKING POLICY
- DROP MATERIALIZED VIEW
- DROP MODEL
- DROP OPERATOR
- DROP OWNED
- DROP PACKAGE
- DROP PROCEDURE
- DROP RESOURCE LABEL
- DROP RESOURCE POOL
- DROP ROW LEVEL SECURITY POLICY
- DROP ROLE
- DROP RULE
- DROP SCHEMA
- DROP SEQUENCE
- DROP SERVER
- DROP SYNONYM
- DROP TABLE
- DROP TABLESPACE
- DROP TEXT SEARCH CONFIGURATION
- DROP TEXT SEARCH DICTIONARY
- DROP TRIGGER
- DROP TYPE
- DROP USER
- DROP USER MAPPING
- DROP VIEW
- DROP WEAK PASSWORD DICTIONARY
- EXECUTE
- EXECUTE DIRECT
- EXPLAIN
- EXPLAIN PLAN
- FETCH
- GRANT
- INSERT
- LOCK
- MOVE
- MERGE INTO
- PREDICT BY
- PREPARE
- PREPARE TRANSACTION
- PURGE
- REASSIGN OWNED
- REFRESH INCREMENTAL MATERIALIZED VIEW
- REFRESH MATERIALIZED VIEW
- REINDEX
- RELEASE SAVEPOINT
- RESET
- REVOKE
- ROLLBACK
- ROLLBACK PREPARED
- ROLLBACK TO SAVEPOINT
- SAVEPOINT
- SELECT
- SELECT INTO
- SET
- SET CONSTRAINTS
- SET ROLE
- SET SESSION AUTHORIZATION
- SET TRANSACTION
- SHOW
- SHUTDOWN
- SNAPSHOT
- START TRANSACTION
- TIMECAPSULE TABLE
- TRUNCATE
- UPDATE
- VACUUM
- VALUES
- SQL Reference
- MogDB SQL
- Keywords
- Constant and Macro
- Expressions
- Type Conversion
- Full Text Search
- Introduction
- Tables and Indexes
- Controlling Text Search
- Additional Features
- Parser
- Dictionaries
- Configuration Examples
- Testing and Debugging Text Search
- Limitations
- System Operation
- Controlling Transactions
- DDL Syntax Overview
- DML Syntax Overview
- DCL Syntax Overview
- Appendix
- GUC Parameters
- GUC Parameter Usage
- File Location
- Connection and Authentication
- Resource Consumption
- Parallel Import
- Write Ahead Log
- HA Replication
- Memory Table
- Query Planning
- Error Reporting and Logging
- Alarm Detection
- Statistics During the Database Running
- Load Management
- Automatic Vacuuming
- Default Settings of Client Connection
- Lock Management
- Version and Platform Compatibility
- Faut Tolerance
- Connection Pool Parameters
- MogDB Transaction
- Developer Options
- Auditing
- Upgrade Parameters
- Miscellaneous Parameters
- Wait Events
- Query
- System Performance Snapshot
- Security Configuration
- Global Temporary Table
- HyperLogLog
- Scheduled Task
- Thread Pool
- User-defined Functions
- Backup and Restoration
- Undo
- DCF Parameters Settings
- Flashback
- Rollback Parameters
- Reserved Parameters
- AI Features
- Appendix
- Schema
- Information Schema
- DBE_PERF
- Overview
- OS
- Instance
- Memory
- File
- Object
- STAT_USER_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STAT_USER_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STAT_USER_TABLES
- STAT_USER_INDEXES
- SUMMARY_STAT_USER_INDEXES
- GLOBAL_STAT_USER_INDEXES
- STAT_SYS_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STAT_SYS_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STAT_SYS_TABLES
- STAT_SYS_INDEXES
- SUMMARY_STAT_SYS_INDEXES
- GLOBAL_STAT_SYS_INDEXES
- STAT_ALL_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STAT_ALL_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STAT_ALL_TABLES
- STAT_ALL_INDEXES
- SUMMARY_STAT_ALL_INDEXES
- GLOBAL_STAT_ALL_INDEXES
- STAT_DATABASE
- SUMMARY_STAT_DATABASE
- GLOBAL_STAT_DATABASE
- STAT_DATABASE_CONFLICTS
- SUMMARY_STAT_DATABASE_CONFLICTS
- GLOBAL_STAT_DATABASE_CONFLICTS
- STAT_XACT_ALL_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STAT_XACT_ALL_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STAT_XACT_ALL_TABLES
- STAT_XACT_SYS_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STAT_XACT_SYS_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STAT_XACT_SYS_TABLES
- STAT_XACT_USER_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STAT_XACT_USER_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STAT_XACT_USER_TABLES
- STAT_XACT_USER_FUNCTIONS
- SUMMARY_STAT_XACT_USER_FUNCTIONS
- GLOBAL_STAT_XACT_USER_FUNCTIONS
- STAT_BAD_BLOCK
- SUMMARY_STAT_BAD_BLOCK
- GLOBAL_STAT_BAD_BLOCK
- STAT_USER_FUNCTIONS
- SUMMARY_STAT_USER_FUNCTIONS
- GLOBAL_STAT_USER_FUNCTIONS
- Workload
- Session/Thread
- SESSION_STAT
- GLOBAL_SESSION_STAT
- SESSION_TIME
- GLOBAL_SESSION_TIME
- SESSION_MEMORY
- GLOBAL_SESSION_MEMORY
- SESSION_MEMORY_DETAIL
- GLOBAL_SESSION_MEMORY_DETAIL
- SESSION_STAT_ACTIVITY
- GLOBAL_SESSION_STAT_ACTIVITY
- THREAD_WAIT_STATUS
- GLOBAL_THREAD_WAIT_STATUS
- LOCAL_THREADPOOL_STATUS
- GLOBAL_THREADPOOL_STATUS
- SESSION_CPU_RUNTIME
- SESSION_MEMORY_RUNTIME
- STATEMENT_IOSTAT_COMPLEX_RUNTIME
- LOCAL_ACTIVE_SESSION
- Transaction
- Query
- STATEMENT
- SUMMARY_STATEMENT
- STATEMENT_COUNT
- GLOBAL_STATEMENT_COUNT
- SUMMARY_STATEMENT_COUNT
- GLOBAL_STATEMENT_COMPLEX_HISTORY
- GLOBAL_STATEMENT_COMPLEX_HISTORY_TABLE
- GLOBAL_STATEMENT_COMPLEX_RUNTIME
- STATEMENT_RESPONSETIME_PERCENTILE
- STATEMENT_USER_COMPLEX_HISTORY
- STATEMENT_COMPLEX_RUNTIME
- STATEMENT_COMPLEX_HISTORY_TABLE
- STATEMENT_COMPLEX_HISTORY
- STATEMENT_WLMSTAT_COMPLEX_RUNTIME
- STATEMENT_HISTORY
- Cache/IO
- STATIO_USER_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_USER_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_USER_TABLES
- STATIO_USER_INDEXES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_USER_INDEXES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_USER_INDEXES
- STATIO_USER_SEQUENCES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_USER_SEQUENCES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_USER_SEQUENCES
- STATIO_SYS_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_SYS_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_SYS_TABLES
- STATIO_SYS_INDEXES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_SYS_INDEXES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_SYS_INDEXES
- STATIO_SYS_SEQUENCES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_SYS_SEQUENCES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_SYS_SEQUENCES
- STATIO_ALL_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_ALL_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_ALL_TABLES
- STATIO_ALL_INDEXES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_ALL_INDEXES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_ALL_INDEXES
- STATIO_ALL_SEQUENCES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_ALL_SEQUENCES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_ALL_SEQUENCES
- GLOBAL_STAT_DB_CU
- GLOBAL_STAT_SESSION_CU
- Utility
- REPLICATION_STAT
- GLOBAL_REPLICATION_STAT
- REPLICATION_SLOTS
- GLOBAL_REPLICATION_SLOTS
- BGWRITER_STAT
- GLOBAL_BGWRITER_STAT
- GLOBAL_CKPT_STATUS
- GLOBAL_DOUBLE_WRITE_STATUS
- GLOBAL_PAGEWRITER_STATUS
- GLOBAL_RECORD_RESET_TIME
- GLOBAL_REDO_STATUS
- GLOBAL_RECOVERY_STATUS
- CLASS_VITAL_INFO
- USER_LOGIN
- SUMMARY_USER_LOGIN
- GLOBAL_GET_BGWRITER_STATUS
- GLOBAL_SINGLE_FLUSH_DW_STATUS
- GLOBAL_CANDIDATE_STATUS
- Lock
- Wait Events
- Configuration
- Operator
- Workload Manager
- Global Plancache
- RTO
- Appendix
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER Schema
- Overview
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.turn_on
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.turn_off
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.local_debug_server_info
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.attach
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.next
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.continue
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.abort
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.print_var
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.info_code
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.step
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.add_breakpoint
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.delete_breakpoint
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.info_breakpoints
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.backtrace
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.finish
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.set_var
- DB4AI Schema
- Tool Reference
- Tool Overview
- Client Tool
- Server Tools
- Tools Used in the Internal System
- gaussdb
- gs_backup
- gs_basebackup
- gs_ctl
- gs_initdb
- gs_install
- gs_install_plugin
- gs_install_plugin_local
- gs_postuninstall
- gs_preinstall
- gs_sshexkey
- gs_tar
- gs_uninstall
- gs_upgradectl
- gs_expansion
- gs_dropnode
- gs_probackup
- gstrace
- kdb5_util
- kadmin.local
- kinit
- klist
- krb5kdc
- kdestroy
- pg_config
- pg_controldata
- pg_recvlogical
- pg_resetxlog
- pg_archivecleanup
- pssh
- pscp
- transfer.py
- FAQ
- System Catalogs and Views Supported by gs_collector
- Extension Reference
- Error Code Reference
- Description of SQL Error Codes
- Third-Party Library Error Codes
- GAUSS-00001 - GAUSS-00100
- GAUSS-00101 - GAUSS-00200
- GAUSS 00201 - GAUSS 00300
- GAUSS 00301 - GAUSS 00400
- GAUSS 00401 - GAUSS 00500
- GAUSS 00501 - GAUSS 00600
- GAUSS 00601 - GAUSS 00700
- GAUSS 00701 - GAUSS 00800
- GAUSS 00801 - GAUSS 00900
- GAUSS 00901 - GAUSS 01000
- GAUSS 01001 - GAUSS 01100
- GAUSS 01101 - GAUSS 01200
- GAUSS 01201 - GAUSS 01300
- GAUSS 01301 - GAUSS 01400
- GAUSS 01401 - GAUSS 01500
- GAUSS 01501 - GAUSS 01600
- GAUSS 01601 - GAUSS 01700
- GAUSS 01701 - GAUSS 01800
- GAUSS 01801 - GAUSS 01900
- GAUSS 01901 - GAUSS 02000
- GAUSS 02001 - GAUSS 02100
- GAUSS 02101 - GAUSS 02200
- GAUSS 02201 - GAUSS 02300
- GAUSS 02301 - GAUSS 02400
- GAUSS 02401 - GAUSS 02500
- GAUSS 02501 - GAUSS 02600
- GAUSS 02601 - GAUSS 02700
- GAUSS 02701 - GAUSS 02800
- GAUSS 02801 - GAUSS 02900
- GAUSS 02901 - GAUSS 03000
- GAUSS 03001 - GAUSS 03100
- GAUSS 03101 - GAUSS 03200
- GAUSS 03201 - GAUSS 03300
- GAUSS 03301 - GAUSS 03400
- GAUSS 03401 - GAUSS 03500
- GAUSS 03501 - GAUSS 03600
- GAUSS 03601 - GAUSS 03700
- GAUSS 03701 - GAUSS 03800
- GAUSS 03801 - GAUSS 03900
- GAUSS 03901 - GAUSS 04000
- GAUSS 04001 - GAUSS 04100
- GAUSS 04101 - GAUSS 04200
- GAUSS 04201 - GAUSS 04300
- GAUSS 04301 - GAUSS 04400
- GAUSS 04401 - GAUSS 04500
- GAUSS 04501 - GAUSS 04600
- GAUSS 04601 - GAUSS 04700
- GAUSS 04701 - GAUSS 04800
- GAUSS 04801 - GAUSS 04900
- GAUSS 04901 - GAUSS 05000
- GAUSS 05001 - GAUSS 05100
- GAUSS 05101 - GAUSS 05200
- GAUSS 05201 - GAUSS 05300
- GAUSS 05301 - GAUSS 05400
- GAUSS 05401 - GAUSS 05500
- GAUSS 05501 - GAUSS 05600
- GAUSS 05601 - GAUSS 05700
- GAUSS 05701 - GAUSS 05800
- GAUSS 05801 - GAUSS 05900
- GAUSS 05901 - GAUSS 06000
- GAUSS 06001 - GAUSS 06100
- GAUSS 06101 - GAUSS 06200
- GAUSS 06201 - GAUSS 06300
- GAUSS 06301 - GAUSS 06400
- GAUSS 06401 - GAUSS 06500
- GAUSS 06501 - GAUSS 06600
- GAUSS 06601 - GAUSS 06700
- GAUSS 06701 - GAUSS 06800
- GAUSS 06801 - GAUSS 06900
- GAUSS 06901 - GAUSS 07000
- GAUSS 07001 - GAUSS 07100
- GAUSS 07101 - GAUSS 07200
- GAUSS 07201 - GAUSS 07300
- GAUSS 07301 - GAUSS 07400
- GAUSS 07401 - GAUSS 07480
- GAUSS 50000 - GAUSS 50999
- GAUSS 51000 - GAUSS 51999
- GAUSS 52000 - GAUSS 52999
- GAUSS 53000 - GAUSS 53699
- Error Log Reference
- System Catalogs and System Views
- Common Faults and Identification Guide
- Common Fault Locating Methods
- Common Fault Locating Cases
- Core Fault Locating
- Permission/Session/Data Type Fault Location
- Service/High Availability/Concurrency Fault Location
- Table/Partition Table Fault Location
- File System/Disk/Memory Fault Location
- After You Run the du Command to Query Data File Size In the XFS File System, the Query Result Is Greater than the Actual File Size
- File Is Damaged in the XFS File System
- Insufficient Memory
- "Error:No space left on device" Is Displayed
- When the TPC-C is running and a disk to be injected is full, the TPC-C stops responding
- Disk Space Usage Reaches the Threshold and the Database Becomes Read-only
- SQL Fault Location
- Index Fault Location
- Source Code Parsing
- FAQs
- Glossary
Column-store Tables Management
What is Column-store
Row-store stores tables to disk partitions by row, and column-store stores tables to disk partitions by column. By default, a row-store table is created. For details about differences between row storage and column storage, see Figure 1.
Figure 1 Differences between row storage and column storage
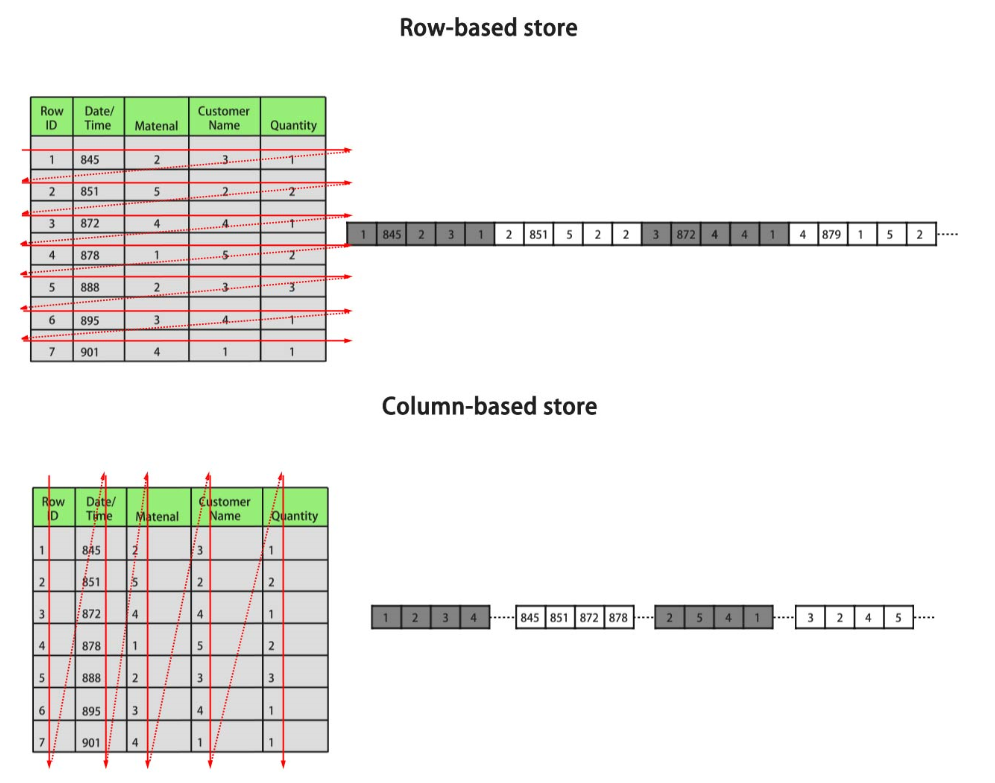
In the preceding figure, the upper left part is a row-store table, and the upper right part shows how the row-store table is stored on a disk; the lower left part is a column-store table, and the lower right part shows how the column-store table is stored on a disk. From the above figure, you can clearly see that the data of a row-store table are put together, but they are kept separately in column-store table.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Row-store and Column-store Tables and Their Usage Scenario
Both storage models have benefits and drawbacks.
| Storage Model | Benefit | Drawback |
|---|---|---|
| Row storage | Record data is stored together. Data can be easily inserted and updated. | All the columns of a record are read after the SELECT statement is executed even if only certain columns are required. |
| Column storage | Only the columns involved in a query are read. Projections are efficient. Any column can serve as an index. | The selected columns need to be reconstructed after the SELECT statement is executed. Data cannot be easily inserted or updated. |
Generally, if a table contains many columns (called a wide table) and its query involves only a few columns, column storage is recommended. Row storage is recommended if a table contains only a few columns and a query involves most of the fields.
| Storage Model | Application Scenarios |
|---|---|
| Row storage | Point queries (simple index-based queries that only return a few records)Scenarios requiring frequent addition, deletion, and modification |
| Column storage | Statistical analysis queries (requiring a large number of association and grouping operations)Ad hoc queries (using uncertain query conditions and unable to utilize indexes to scan row-store tables) |
MogDB supports hybrid row storage and column storage. Each storage model applies to specific scenarios. Select an appropriate model when creating a table. Generally, MogDB is used for transactional processing databases. By default, row storage is used. Column storage is used only when complex queries in large data volume are performed.
Selecting a Storage Model
-
Update frequency
If data is frequently updated, use a row-store table.
-
Data insertion frequency
If a small amount of data is frequently inserted each time, use a row-store table.
-
Number of columns
If a table is to contain many columns, use a column-store table.
-
Number of columns to be queried
If only a small number of columns (less than 50% of the total) is queried each time, use a column-store table.
-
Compression ratio
The compression ratio of a column-store table is higher than that of a row-store table. High compression ratio consumes more CPU resources.
Constraints of Column-store Table
- The column-store table does not support arrays.
- The number of column-store tables is recommended to be no more than 1000.
- The table-level constraints of the column-store table only support PARTIAL CLUSTER KEY, and do not support table-level constraints such as primary and foreign keys.
- The field constraints of the column-store table only support NULL, NOT NULL and DEFAULT constant values.
- The column-store table does not support the alter command to modify field constraints.
- The column-store table supports the delta table, which is controlled by the parameter enable_delta_store whether to enable or not, and the threshold value for entering the delta table is controlled by the parameter deltarow_threshold.
Related Parameters
-
cstore_buffers
The size of the shared buffer used by the column-store, the default value: 32768KB.
-
partition_mem_batch
Specify the number of caches. In order to optimize the batch insertion of column-store partition tables, the data will be cached during the batch insertion process and then written to disk in batches. Default value: 256.
-
partition_max_cache_size
Specify the size of the data buffer area. In order to optimize the batch insertion of column-store partition tables, the data will be cached during the batch insertion process and then written to disk in batches. Default value: 2GB.
-
enable_delta_store
In order to enhance the performance of single data import in column-store and solve the problem of disk redundancy, whether it is necessary to enable the function of column-store delta table and use it in conjunction with the parameter DELTAROW_THRESHOLD. Default value: off.
Create Table Commands
MogDB creates normal tables as uncompressed row-store tables by default.
mogdb=# \dt
No relations found.
mogdb=# create table test_t(id serial primary key ,col1 varchar(8),col2 decimal(6,2),create_time timestamptz not null default now());
NOTICE: CREATE TABLE will create implicit sequence "test_t_id_seq" for serial column "test_t.id"
NOTICE: CREATE TABLE / PRIMARY KEY will create implicit index "test_t_pkey" for table "test_t"
CREATE TABLE
mogdb=# \dt+
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner | Size | Storage | Description
--------+--------+-------+-------+---------+----------------------------------+-------------
public | test_t | table | omm | 0 bytes | {orientation=row,compression=no} |
(1 row)
mogdb=#To create a column-store table, you need to specify orientation=column, the default compression level is low.
mogdb=# create table column_t(id serial,col1 varchar(8),col2 decimal(6,2),create_time timestamptz not null default now()) with (orientation=column );
NOTICE: CREATE TABLE will create implicit sequence "column_t_id_seq" for serial column "column_t.id"
CREATE TABLE
mogdb=# \dt+
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner | Size | Storage | Description
--------+----------+-------+-------+---------+--------------------------------------+-------------
public | column_t | table | omm | 16 kB | {orientation=column,compression=low} |
public | test_t | table | omm | 0 bytes | {orientation=row,compression=no} |
(2 rows)
mogdb=# \d+ column_t
Table "public.column_t"
Column | Type | Modifiers | Storage | Stats target | Description
-------------+--------------------------+-------------------------------------------------------+----------+--------------+-------------
id | integer | not null default nextval('column_t_id_seq'::regclass) | plain | |
col1 | character varying(8) | | extended | |
col2 | numeric(6,2) | | main | |
create_time | timestamp with time zone | not null default now() | plain | |
Has OIDs: no
Options: orientation=column, compression=lowAdd partial clustered storage columns to the column-store table.
mogdb=# \d+ column_t
Table "public.column_t"
Column | Type | Modifiers | Storage | Stats target | Description
-------------+--------------------------+-------------------------------------------------------+----------+--------------+-------------
id | integer | not null default nextval('column_t_id_seq'::regclass) | plain | |
col1 | character varying(8) | | extended | |
col2 | numeric(6,2) | | main | |
create_time | timestamp with time zone | not null default now() | plain | |
Has OIDs: no
Options: orientation=column, compression=low
mogdb=# alter table column_t add PARTIAL CLUSTER KEY(id);
ALTER TABLE
mogdb=# \d+ column_t
Table "public.column_t"
Column | Type | Modifiers | Storage | Stats target | Description
-------------+--------------------------+-------------------------------------------------------+----------+--------------+-------------
id | integer | not null default nextval('column_t_id_seq'::regclass) | plain | |
col1 | character varying(8) | | extended | |
col2 | numeric(6,2) | | main | |
create_time | timestamp with time zone | not null default now() | plain | |
Partial Cluster :
"column_t_cluster" PARTIAL CLUSTER KEY (id)
Has OIDs: no
Options: orientation=column, compression=low
mogdb=#Create column-store tables with partial clustered storage directly.
mogdb=# create table column_c(id serial,col1 varchar(8),col2 decimal(6,2),create_time timestamptz not null default now(),PARTIAL CLUSTER KEY(id)) with (orientation=column );
NOTICE: CREATE TABLE will create implicit sequence "column_c_id_seq" for serial column "column_c.id"
CREATE TABLE
mogdb=# \d+ column_c
Table "public.column_c"
Column | Type | Modifiers | Storage | Stats target | Description
-------------+--------------------------+-------------------------------------------------------+----------+--------------+-------------
id | integer | not null default nextval('column_c_id_seq'::regclass) | plain | |
col1 | character varying(8) | | extended | |
col2 | numeric(6,2) | | main | |
create_time | timestamp with time zone | not null default now() | plain | |
Partial Cluster :
"column_c_cluster" PARTIAL CLUSTER KEY (id)
Has OIDs: no
Options: orientation=column, compression=low
mogdb=#Please refer to Supported Data Types > Data Types Supported by Column-store Tables under the Reference Guide for the data types supported by column-store tables.
Column-store versus Row-store
Used disk space
-
The default size of the column-store table is 16K, the compression level is low.
-
The default size of the row-store table is 0bytes, the compression level is no.
-
Insert 1 million pieces of data into the two tables separately , and compare the occupied disk size.
mogdb=# \dt+ List of relations Schema | Name | Type | Owner | Size | Storage | Description --------+-----------+-------+-------+---------+-----------------------------------------+------------- public | column_t | table | omm | 16 kB | {orientation=column,compression=low} | public | column_th | table | omm | 16 kB | {orientation=column,compression=high} | public | column_tm | table | omm | 16 kB | {orientation=column,compression=middle} | public | row_tc | table | omm | 0 bytes | {orientation=row,compression=yes} | public | test_t | table | omm | 0 bytes | {orientation=row,compression=no} | (5 rows) mogdb=# insert into column_t select generate_series(1,1000000),left(md5(random()::text),8),random()::numeric(6,2); INSERT 0 1000000 Time: 11328.880 ms mogdb=# insert into column_th select generate_series(1,1000000),left(md5(random()::text),8),random()::numeric(6,2); INSERT 0 1000000 Time: 10188.634 ms mogdb=# insert into column_tm select generate_series(1,1000000),left(md5(random()::text),8),random()::numeric(6,2); INSERT 0 1000000 Time: 9802.739 ms mogdb=# insert into test_t select generate_series(1,1000000),left(md5(random()::text),8),random()::numeric(6,2); INSERT 0 1000000 Time: 17404.945 ms mogdb=# insert into row_tc select generate_series(1,1000000),left(md5(random()::text),8),random()::numeric(6,2); INSERT 0 1000000 Time: 12394.866 ms mogdb=# \dt+ List of relations Schema | Name | Type | Owner | Size | Storage | Description --------+-----------+-------+-------+----------+-----------------------------------------+------------- public | column_t | table | omm | 12 MB | {orientation=column,compression=low} | public | column_th | table | omm | 8304 kB | {orientation=column,compression=high} | public | column_tm | table | omm | 10168 kB | {orientation=column,compression=middle} | public | row_tc | table | omm | 58 MB | {orientation=row,compression=yes} | public | test_t | table | omm | 58 MB | {orientation=row,compression=no} | (5 rows) mogdb=# -
The higher the compression level of the column-store table is, the less the disk space it uses.
-
After the row-store table is compressed, the size of the disk space dose not decrease significantly.
-
Column-store table take up nearly 6 times less disk space than row-store table.
DML Comparison
Search for a single column:
---
---Search by range, column-store is nearly 20 times faster than row-store
---
mogdb=# select col1 from test_t where id>=100010 and id<100020;
col1
----------
4257a3f3
3d397284
64343438
6eb7bdb7
d1c9073d
6aeb037c
1d424974
223235ab
329de235
2f02adc1
(10 rows)
Time: 77.341 ms
mogdb=# select col1 from column_t where id>=100010 and id<100020;
col1
----------
d4837c30
87a46f7a
2f42a9c9
4481c793
68800204
613b9205
9d8f4a0a
5cc4ff9e
f948cd10
f2775cee
(10 rows)
Time: 3.884 ms
---
---Search Randomly, column-store is nearly 35 times faster than row-store
---
mogdb=# select col1 from test_t limit 10;
col1
----------
c2780d93
294be14d
4e53b761
2c10f8a2
ae776743
7d683c66
b3b40054
7e56edf9
a7b7336e
ea3d47d9
(10 rows)
Time: 249.887 ms
mogdb=# select col1 from column_t limit 10;
col1
----------
a745d77b
4b6df494
76fed9c1
70c9664d
3384de8a
4158f3bf
5d1c3b9f
341876bb
f396f4ed
abfd78bb
(10 rows)
Time: 7.738 msSearch for all the data:
---
---Row-store is 30% faster than column-store search
---
mogdb=# select * from test_t limit 10;
id | col1 | col2 | create_time
----+----------+------+-------------------------------
1 | c2780d93 | .37 | 2020-10-26 14:27:33.304108+08
2 | 294be14d | .57 | 2020-10-26 14:27:33.304108+08
3 | 4e53b761 | .98 | 2020-10-26 14:27:33.304108+08
4 | 2c10f8a2 | .27 | 2020-10-26 14:27:33.304108+08
5 | ae776743 | .97 | 2020-10-26 14:27:33.304108+08
6 | 7d683c66 | .58 | 2020-10-26 14:27:33.304108+08
7 | b3b40054 | .44 | 2020-10-26 14:27:33.304108+08
8 | 7e56edf9 | .43 | 2020-10-26 14:27:33.304108+08
9 | a7b7336e | .31 | 2020-10-26 14:27:33.304108+08
10 | ea3d47d9 | .42 | 2020-10-26 14:27:33.304108+08
(10 rows)
Time: 6.822 ms
mogdb=# select * from column_t limit 10;
id | col1 | col2 | create_time
----+----------+------+-------------------------------
1 | a745d77b | .33 | 2020-10-26 14:28:20.633253+08
2 | 4b6df494 | .42 | 2020-10-26 14:28:20.633253+08
3 | 76fed9c1 | .73 | 2020-10-26 14:28:20.633253+08
4 | 70c9664d | .74 | 2020-10-26 14:28:20.633253+08
5 | 3384de8a | .48 | 2020-10-26 14:28:20.633253+08
6 | 4158f3bf | .59 | 2020-10-26 14:28:20.633253+08
7 | 5d1c3b9f | .63 | 2020-10-26 14:28:20.633253+08
8 | 341876bb | .97 | 2020-10-26 14:28:20.633253+08
9 | f396f4ed | .73 | 2020-10-26 14:28:20.633253+08
10 | abfd78bb | .30 | 2020-10-26 14:28:20.633253+08
(10 rows)
Time: 9.982 msUpdate data:
---
---Update a field directly, column-store is nearly 7 times faster than row-store
---
mogdb=# update test_t set col1=col1;
UPDATE 1000000
Time: 19779.978 ms
mogdb=# update column_t set col1=col1;
UPDATE 1000000
Time: 2702.339 msConclusion
- The Column-store table saves nearly 6 times the disk space usage compared to the row-store table.
- When searching for the specified field, the column-store table is about 20-35 times faster than the row-store table.
- When searching for all the data, the column-store table is 30% slower than the row-store table.
- When importing data in batches in the default compression mode, and column-store table is 40% faster than the row-store table.