- About MogDB
- Quick Start
- MogDB Playground
- Container-based MogDB Installation
- Installation on a Single Node
- MogDB Access
- Use CLI to Access MogDB
- Use GUI to Access MogDB
- Use Middleware to Access MogDB
- Use Programming Language to Access MogDB
- Using Sample Dataset Mogila
- Characteristic Description
- High Performance
- High Availability (HA)
- Maintainability
- Database Security
- Access Control Model
- Separation of Control and Access Permissions
- Database Encryption Authentication
- Data Encryption and Storage
- Database Audit
- Network Communication Security
- Resource Label
- Unified Audit
- Dynamic Data Anonymization
- Row-Level Access Control
- Password Strength Verification
- Equality Query in a Fully-encrypted Database
- Ledger Database Mechanism
- Enterprise-Level Features
- Support for Functions and Stored Procedures
- SQL Hints
- Full-Text Indexing
- Copy Interface for Error Tolerance
- Partitioning
- Support for Advanced Analysis Functions
- Materialized View
- HyperLogLog
- Creating an Index Online
- Autonomous Transaction
- Global Temporary Table
- Pseudocolumn ROWNUM
- Stored Procedure Debugging
- JDBC Client Load Balancing and Read/Write Isolation
- In-place Update Storage Engine
- Application Development Interfaces
- AI Capabilities
- Installation Guide
- Container Installation
- Simplified Installation Process
- Standard Installation
- Manual Installation
- Administrator Guide
- Routine Maintenance
- Starting and Stopping MogDB
- Using the gsql Client for Connection
- Routine Maintenance
- Checking OS Parameters
- Checking MogDB Health Status
- Checking Database Performance
- Checking and Deleting Logs
- Checking Time Consistency
- Checking The Number of Application Connections
- Routinely Maintaining Tables
- Routinely Recreating an Index
- Data Security Maintenance Suggestions
- Log Reference
- Primary and Standby Management
- MOT Engine
- Introducing MOT
- Using MOT
- Concepts of MOT
- Appendix
- Column-store Tables Management
- Backup and Restoration
- Importing and Exporting Data
- Importing Data
- Exporting Data
- Upgrade Guide
- Routine Maintenance
- AI Features Guide
- Overview
- Predictor: AI Query Time Forecasting
- X-Tuner: Parameter Optimization and Diagnosis
- SQLdiag: Slow SQL Discovery
- A-Detection: Status Monitoring
- Index-advisor: Index Recommendation
- DeepSQL
- AI-Native Database (DB4AI)
- Security Guide
- Developer Guide
- Application Development Guide
- Development Specifications
- Development Based on JDBC
- Overview
- JDBC Package, Driver Class, and Environment Class
- Development Process
- Loading the Driver
- Connecting to a Database
- Connecting to the Database (Using SSL)
- Running SQL Statements
- Processing Data in a Result Set
- Closing a Connection
- Managing Logs
- Example: Common Operations
- Example: Retrying SQL Queries for Applications
- Example: Importing and Exporting Data Through Local Files
- Example 2: Migrating Data from a MY Database to MogDB
- Example: Logic Replication Code
- Example: Parameters for Connecting to the Database in Different Scenarios
- JDBC API Reference
- java.sql.Connection
- java.sql.CallableStatement
- java.sql.DatabaseMetaData
- java.sql.Driver
- java.sql.PreparedStatement
- java.sql.ResultSet
- java.sql.ResultSetMetaData
- java.sql.Statement
- javax.sql.ConnectionPoolDataSource
- javax.sql.DataSource
- javax.sql.PooledConnection
- javax.naming.Context
- javax.naming.spi.InitialContextFactory
- CopyManager
- Development Based on ODBC
- Development Based on libpq
- Development Based on libpq
- libpq API Reference
- Database Connection Control Functions
- Database Statement Execution Functions
- Functions for Asynchronous Command Processing
- Functions for Canceling Queries in Progress
- Example
- Connection Characters
- Psycopg-Based Development
- Commissioning
- Appendices
- Stored Procedure
- User Defined Functions
- PL/pgSQL-SQL Procedural Language
- Scheduled Jobs
- Autonomous Transaction
- Logical Replication
- Logical Decoding
- Foreign Data Wrapper
- Materialized View
- Materialized View Overview
- Full Materialized View
- Incremental Materialized View
- Resource Load Management
- Overview
- Resource Management Preparation
- Application Development Guide
- Performance Tuning Guide
- System Optimization
- SQL Optimization
- WDR Snapshot Schema
- TPCC Performance Tuning Guide
- Reference Guide
- System Catalogs and System Views
- Overview of System Catalogs and System Views
- System Catalogs
- GS_AUDITING_POLICY
- GS_AUDITING_POLICY_ACCESS
- GS_AUDITING_POLICY_FILTERS
- GS_AUDITING_POLICY_PRIVILEGES
- GS_CLIENT_GLOBAL_KEYS
- GS_CLIENT_GLOBAL_KEYS_ARGS
- GS_COLUMN_KEYS
- GS_COLUMN_KEYS_ARGS
- GS_ENCRYPTED_COLUMNS
- GS_ENCRYPTED_PROC
- GS_GLOBAL_CHAIN
- GS_MASKING_POLICY
- GS_MASKING_POLICY_ACTIONS
- GS_MASKING_POLICY_FILTERS
- GS_MATVIEW
- GS_MATVIEW_DEPENDENCY
- GS_OPT_MODEL
- GS_POLICY_LABEL
- GS_RECYCLEBIN
- GS_TXN_SNAPSHOT
- GS_WLM_INSTANCE_HISTORY
- GS_WLM_OPERATOR_INFO
- GS_WLM_PLAN_ENCODING_TABLE
- GS_WLM_PLAN_OPERATOR_INFO
- GS_WLM_EC_OPERATOR_INFO
- PG_AGGREGATE
- PG_AM
- PG_AMOP
- PG_AMPROC
- PG_APP_WORKLOADGROUP_MAPPING
- PG_ATTRDEF
- PG_ATTRIBUTE
- PG_AUTHID
- PG_AUTH_HISTORY
- PG_AUTH_MEMBERS
- PG_CAST
- PG_CLASS
- PG_COLLATION
- PG_CONSTRAINT
- PG_CONVERSION
- PG_DATABASE
- PG_DB_ROLE_SETTING
- PG_DEFAULT_ACL
- PG_DEPEND
- PG_DESCRIPTION
- PG_DIRECTORY
- PG_ENUM
- PG_EXTENSION
- PG_EXTENSION_DATA_SOURCE
- PG_FOREIGN_DATA_WRAPPER
- PG_FOREIGN_SERVER
- PG_FOREIGN_TABLE
- PG_INDEX
- PG_INHERITS
- PG_JOB
- PG_JOB_PROC
- PG_LANGUAGE
- PG_LARGEOBJECT
- PG_LARGEOBJECT_METADATA
- PG_NAMESPACE
- PG_OBJECT
- PG_OPCLASS
- PG_OPERATOR
- PG_OPFAMILY
- PG_PARTITION
- PG_PLTEMPLATE
- PG_PROC
- PG_RANGE
- PG_RESOURCE_POOL
- PG_REWRITE
- PG_RLSPOLICY
- PG_SECLABEL
- PG_SHDEPEND
- PG_SHDESCRIPTION
- PG_SHSECLABEL
- PG_STATISTIC
- PG_STATISTIC_EXT
- PG_SYNONYM
- PG_TABLESPACE
- PG_TRIGGER
- PG_TS_CONFIG
- PG_TS_CONFIG_MAP
- PG_TS_DICT
- PG_TS_PARSER
- PG_TS_TEMPLATE
- PG_TYPE
- PG_USER_MAPPING
- PG_USER_STATUS
- PG_WORKLOAD_GROUP
- PLAN_TABLE_DATA
- STATEMENT_HISTORY
- System Views
- GET_GLOBAL_PREPARED_XACTS
- GS_AUDITING
- GS_AUDITING_ACCESS
- GS_AUDITING_PRIVILEGE
- GS_CLUSTER_RESOURCE_INFO
- GS_INSTANCE_TIME
- GS_LABELS
- GS_MASKING
- GS_MATVIEWS
- GS_SESSION_MEMORY
- GS_SESSION_CPU_STATISTICS
- GS_SESSION_MEMORY_CONTEXT
- GS_SESSION_MEMORY_DETAIL
- GS_SESSION_MEMORY_STATISTICS
- GS_SQL_COUNT
- GS_WLM_CGROUP_INFO
- GS_WLM_PLAN_OPERATOR_HISTORY
- GS_WLM_REBUILD_USER_RESOURCE_POOL
- GS_WLM_RESOURCE_POOL
- GS_WLM_USER_INFO
- GS_STAT_SESSION_CU
- GS_TOTAL_MEMORY_DETAIL
- MPP_TABLES
- PG_AVAILABLE_EXTENSION_VERSIONS
- PG_AVAILABLE_EXTENSIONS
- PG_COMM_DELAY
- PG_COMM_RECV_STREAM
- PG_COMM_SEND_STREAM
- PG_COMM_STATUS
- PG_CONTROL_GROUP_CONFIG
- PG_CURSORS
- PG_EXT_STATS
- PG_GET_INVALID_BACKENDS
- PG_GET_SENDERS_CATCHUP_TIME
- PG_GROUP
- PG_GTT_RELSTATS
- PG_GTT_STATS
- PG_GTT_ATTACHED_PIDS
- PG_INDEXES
- PG_LOCKS
- PG_NODE_ENV
- PG_OS_THREADS
- PG_PREPARED_STATEMENTS
- PG_PREPARED_XACTS
- PG_REPLICATION_SLOTS
- PG_RLSPOLICIES
- PG_ROLES
- PG_RULES
- PG_SECLABELS
- PG_SETTINGS
- PG_SHADOW
- PG_STATS
- PG_STAT_ACTIVITY
- PG_STAT_ALL_INDEXES
- PG_STAT_ALL_TABLES
- PG_STAT_BAD_BLOCK
- PG_STAT_BGWRITER
- PG_STAT_DATABASE
- PG_STAT_DATABASE_CONFLICTS
- PG_STAT_USER_FUNCTIONS
- PG_STAT_USER_INDEXES
- PG_STAT_USER_TABLES
- PG_STAT_REPLICATION
- PG_STAT_SYS_INDEXES
- PG_STAT_SYS_TABLES
- PG_STAT_XACT_ALL_TABLES
- PG_STAT_XACT_SYS_TABLES
- PG_STAT_XACT_USER_FUNCTIONS
- PG_STAT_XACT_USER_TABLES
- PG_STATIO_ALL_INDEXES
- PG_STATIO_ALL_SEQUENCES
- PG_STATIO_ALL_TABLES
- PG_STATIO_SYS_INDEXES
- PG_STATIO_SYS_SEQUENCES
- PG_STATIO_SYS_TABLES
- PG_STATIO_USER_INDEXES
- PG_STATIO_USER_SEQUENCES
- PG_STATIO_USER_TABLES
- PG_TABLES
- PG_TDE_INFO
- PG_THREAD_WAIT_STATUS
- PG_TIMEZONE_ABBREVS
- PG_TIMEZONE_NAMES
- PG_TOTAL_MEMORY_DETAIL
- PG_TOTAL_USER_RESOURCE_INFO
- PG_TOTAL_USER_RESOURCE_INFO_OID
- PG_USER
- PG_USER_MAPPINGS
- PG_VARIABLE_INFO
- PG_VIEWS
- PLAN_TABLE
- GS_FILE_STAT
- GS_OS_RUN_INFO
- GS_REDO_STAT
- GS_SESSION_STAT
- GS_SESSION_TIME
- GS_THREAD_MEMORY_CONTEXT
- Functions and Operators
- Logical Operators
- Comparison Operators
- Character Processing Functions and Operators
- Binary String Functions and Operators
- Bit String Functions and Operators
- Mode Matching Operators
- Mathematical Functions and Operators
- Date and Time Processing Functions and Operators
- Type Conversion Functions
- Geometric Functions and Operators
- Network Address Functions and Operators
- Text Search Functions and Operators
- JSON/JSONB Functions and Operators
- HLL Functions and Operators
- SEQUENCE Functions
- Array Functions and Operators
- Range Functions and Operators
- Aggregate Functions
- Window Functions
- Security Functions
- Ledger Database Functions
- Encrypted Equality Functions
- Set Returning Functions
- Conditional Expression Functions
- System Information Functions
- System Administration Functions
- Configuration Settings Functions
- Universal File Access Functions
- Server Signal Functions
- Backup and Restoration Control Functions
- Snapshot Synchronization Functions
- Database Object Functions
- Advisory Lock Functions
- Logical Replication Functions
- Segment-Page Storage Functions
- Other Functions
- Undo System Functions
- Statistics Information Functions
- Trigger Functions
- Hash Function
- Prompt Message Function
- Global Temporary Table Functions
- Fault Injection System Function
- AI Feature Functions
- Dynamic Data Masking Functions
- Other System Functions
- Internal Functions
- Obsolete Functions
- Supported Data Types
- Numeric Types
- Monetary Types
- Boolean Types
- Enumerated Types
- Character Types
- Binary Types
- Date/Time Types
- Geometric
- Network Address Types
- Bit String Types
- Text Search Types
- UUID
- JSON/JSONB Types
- HLL
- Array Types
- Range
- OID Types
- Pseudo-Types
- Data Types Supported by Column-store Tables
- XML Types
- Data Type Used by the Ledger Database
- SQL Syntax
- ABORT
- ALTER AGGREGATE
- ALTER AUDIT POLICY
- ALTER DATABASE
- ALTER DATA SOURCE
- ALTER DEFAULT PRIVILEGES
- ALTER DIRECTORY
- ALTER EXTENSION
- ALTER FOREIGN TABLE
- ALTER FUNCTION
- ALTER GROUP
- ALTER INDEX
- ALTER LANGUAGE
- ALTER LARGE OBJECT
- ALTER MASKING POLICY
- ALTER MATERIALIZED VIEW
- ALTER OPERATOR
- ALTER RESOURCE LABEL
- ALTER RESOURCE POOL
- ALTER ROLE
- ALTER ROW LEVEL SECURITY POLICY
- ALTER RULE
- ALTER SCHEMA
- ALTER SEQUENCE
- ALTER SERVER
- ALTER SESSION
- ALTER SYNONYM
- ALTER SYSTEM KILL SESSION
- ALTER SYSTEM SET
- ALTER TABLE
- ALTER TABLE PARTITION
- ALTER TABLE SUBPARTITION
- ALTER TABLESPACE
- ALTER TEXT SEARCH CONFIGURATION
- ALTER TEXT SEARCH DICTIONARY
- ALTER TRIGGER
- ALTER TYPE
- ALTER USER
- ALTER USER MAPPING
- ALTER VIEW
- ANALYZE | ANALYSE
- BEGIN
- CALL
- CHECKPOINT
- CLEAN CONNECTION
- CLOSE
- CLUSTER
- COMMENT
- COMMIT | END
- COMMIT PREPARED
- CONNECT BY
- COPY
- CREATE AGGREGATE
- CREATE AUDIT POLICY
- CREATE CAST
- CREATE CLIENT MASTER KEY
- CREATE COLUMN ENCRYPTION KEY
- CREATE DATABASE
- CREATE DATA SOURCE
- CREATE DIRECTORY
- CREATE EXTENSION
- CREATE FOREIGN TABLE
- CREATE FUNCTION
- CREATE GROUP
- CREATE INCREMENTAL MATERIALIZED VIEW
- CREATE INDEX
- CREATE LANGUAGE
- CREATE MASKING POLICY
- CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW
- CREATE MODEL
- CREATE OPERATOR
- CREATE PACKAGE
- CREATE ROW LEVEL SECURITY POLICY
- CREATE PROCEDURE
- CREATE RESOURCE LABEL
- CREATE RESOURCE POOL
- CREATE ROLE
- CREATE RULE
- CREATE SCHEMA
- CREATE SEQUENCE
- CREATE SERVER
- CREATE SYNONYM
- CREATE TABLE
- CREATE TABLE AS
- CREATE TABLE PARTITION
- CREATE TABLE SUBPARTITION
- CREATE TABLESPACE
- CREATE TEXT SEARCH CONFIGURATION
- CREATE TEXT SEARCH DICTIONARY
- CREATE TRIGGER
- CREATE TYPE
- CREATE USER
- CREATE USER MAPPING
- CREATE VIEW
- CREATE WEAK PASSWORD DICTIONARY
- CURSOR
- DEALLOCATE
- DECLARE
- DELETE
- DO
- DROP AGGREGATE
- DROP AUDIT POLICY
- DROP CAST
- DROP CLIENT MASTER KEY
- DROP COLUMN ENCRYPTION KEY
- DROP DATABASE
- DROP DATA SOURCE
- DROP DIRECTORY
- DROP EXTENSION
- DROP FOREIGN TABLE
- DROP FUNCTION
- DROP GROUP
- DROP INDEX
- DROP LANGUAGE
- DROP MASKING POLICY
- DROP MATERIALIZED VIEW
- DROP MODEL
- DROP OPERATOR
- DROP OWNED
- DROP PACKAGE
- DROP PROCEDURE
- DROP RESOURCE LABEL
- DROP RESOURCE POOL
- DROP ROW LEVEL SECURITY POLICY
- DROP ROLE
- DROP RULE
- DROP SCHEMA
- DROP SEQUENCE
- DROP SERVER
- DROP SYNONYM
- DROP TABLE
- DROP TABLESPACE
- DROP TEXT SEARCH CONFIGURATION
- DROP TEXT SEARCH DICTIONARY
- DROP TRIGGER
- DROP TYPE
- DROP USER
- DROP USER MAPPING
- DROP VIEW
- DROP WEAK PASSWORD DICTIONARY
- EXECUTE
- EXECUTE DIRECT
- EXPLAIN
- EXPLAIN PLAN
- FETCH
- GRANT
- INSERT
- LOCK
- MOVE
- MERGE INTO
- PREDICT BY
- PREPARE
- PREPARE TRANSACTION
- PURGE
- REASSIGN OWNED
- REFRESH INCREMENTAL MATERIALIZED VIEW
- REFRESH MATERIALIZED VIEW
- REINDEX
- RELEASE SAVEPOINT
- RESET
- REVOKE
- ROLLBACK
- ROLLBACK PREPARED
- ROLLBACK TO SAVEPOINT
- SAVEPOINT
- SELECT
- SELECT INTO
- SET
- SET CONSTRAINTS
- SET ROLE
- SET SESSION AUTHORIZATION
- SET TRANSACTION
- SHOW
- SHUTDOWN
- SNAPSHOT
- START TRANSACTION
- TIMECAPSULE TABLE
- TRUNCATE
- UPDATE
- VACUUM
- VALUES
- SQL Reference
- MogDB SQL
- Keywords
- Constant and Macro
- Expressions
- Type Conversion
- Full Text Search
- Introduction
- Tables and Indexes
- Controlling Text Search
- Additional Features
- Parser
- Dictionaries
- Configuration Examples
- Testing and Debugging Text Search
- Limitations
- System Operation
- Controlling Transactions
- DDL Syntax Overview
- DML Syntax Overview
- DCL Syntax Overview
- Appendix
- GUC Parameters
- GUC Parameter Usage
- File Location
- Connection and Authentication
- Resource Consumption
- Parallel Import
- Write Ahead Log
- HA Replication
- Memory Table
- Query Planning
- Error Reporting and Logging
- Alarm Detection
- Statistics During the Database Running
- Load Management
- Automatic Vacuuming
- Default Settings of Client Connection
- Lock Management
- Version and Platform Compatibility
- Faut Tolerance
- Connection Pool Parameters
- MogDB Transaction
- Developer Options
- Auditing
- Upgrade Parameters
- Miscellaneous Parameters
- Wait Events
- Query
- System Performance Snapshot
- Security Configuration
- Global Temporary Table
- HyperLogLog
- Scheduled Task
- Thread Pool
- User-defined Functions
- Backup and Restoration
- Undo
- DCF Parameters Settings
- Flashback
- Rollback Parameters
- Reserved Parameters
- AI Features
- Appendix
- Schema
- Information Schema
- DBE_PERF
- Overview
- OS
- Instance
- Memory
- File
- Object
- STAT_USER_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STAT_USER_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STAT_USER_TABLES
- STAT_USER_INDEXES
- SUMMARY_STAT_USER_INDEXES
- GLOBAL_STAT_USER_INDEXES
- STAT_SYS_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STAT_SYS_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STAT_SYS_TABLES
- STAT_SYS_INDEXES
- SUMMARY_STAT_SYS_INDEXES
- GLOBAL_STAT_SYS_INDEXES
- STAT_ALL_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STAT_ALL_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STAT_ALL_TABLES
- STAT_ALL_INDEXES
- SUMMARY_STAT_ALL_INDEXES
- GLOBAL_STAT_ALL_INDEXES
- STAT_DATABASE
- SUMMARY_STAT_DATABASE
- GLOBAL_STAT_DATABASE
- STAT_DATABASE_CONFLICTS
- SUMMARY_STAT_DATABASE_CONFLICTS
- GLOBAL_STAT_DATABASE_CONFLICTS
- STAT_XACT_ALL_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STAT_XACT_ALL_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STAT_XACT_ALL_TABLES
- STAT_XACT_SYS_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STAT_XACT_SYS_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STAT_XACT_SYS_TABLES
- STAT_XACT_USER_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STAT_XACT_USER_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STAT_XACT_USER_TABLES
- STAT_XACT_USER_FUNCTIONS
- SUMMARY_STAT_XACT_USER_FUNCTIONS
- GLOBAL_STAT_XACT_USER_FUNCTIONS
- STAT_BAD_BLOCK
- SUMMARY_STAT_BAD_BLOCK
- GLOBAL_STAT_BAD_BLOCK
- STAT_USER_FUNCTIONS
- SUMMARY_STAT_USER_FUNCTIONS
- GLOBAL_STAT_USER_FUNCTIONS
- Workload
- Session/Thread
- SESSION_STAT
- GLOBAL_SESSION_STAT
- SESSION_TIME
- GLOBAL_SESSION_TIME
- SESSION_MEMORY
- GLOBAL_SESSION_MEMORY
- SESSION_MEMORY_DETAIL
- GLOBAL_SESSION_MEMORY_DETAIL
- SESSION_STAT_ACTIVITY
- GLOBAL_SESSION_STAT_ACTIVITY
- THREAD_WAIT_STATUS
- GLOBAL_THREAD_WAIT_STATUS
- LOCAL_THREADPOOL_STATUS
- GLOBAL_THREADPOOL_STATUS
- SESSION_CPU_RUNTIME
- SESSION_MEMORY_RUNTIME
- STATEMENT_IOSTAT_COMPLEX_RUNTIME
- LOCAL_ACTIVE_SESSION
- Transaction
- Query
- STATEMENT
- SUMMARY_STATEMENT
- STATEMENT_COUNT
- GLOBAL_STATEMENT_COUNT
- SUMMARY_STATEMENT_COUNT
- GLOBAL_STATEMENT_COMPLEX_HISTORY
- GLOBAL_STATEMENT_COMPLEX_HISTORY_TABLE
- GLOBAL_STATEMENT_COMPLEX_RUNTIME
- STATEMENT_RESPONSETIME_PERCENTILE
- STATEMENT_USER_COMPLEX_HISTORY
- STATEMENT_COMPLEX_RUNTIME
- STATEMENT_COMPLEX_HISTORY_TABLE
- STATEMENT_COMPLEX_HISTORY
- STATEMENT_WLMSTAT_COMPLEX_RUNTIME
- STATEMENT_HISTORY
- Cache/IO
- STATIO_USER_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_USER_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_USER_TABLES
- STATIO_USER_INDEXES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_USER_INDEXES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_USER_INDEXES
- STATIO_USER_SEQUENCES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_USER_SEQUENCES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_USER_SEQUENCES
- STATIO_SYS_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_SYS_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_SYS_TABLES
- STATIO_SYS_INDEXES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_SYS_INDEXES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_SYS_INDEXES
- STATIO_SYS_SEQUENCES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_SYS_SEQUENCES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_SYS_SEQUENCES
- STATIO_ALL_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_ALL_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_ALL_TABLES
- STATIO_ALL_INDEXES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_ALL_INDEXES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_ALL_INDEXES
- STATIO_ALL_SEQUENCES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_ALL_SEQUENCES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_ALL_SEQUENCES
- GLOBAL_STAT_DB_CU
- GLOBAL_STAT_SESSION_CU
- Utility
- REPLICATION_STAT
- GLOBAL_REPLICATION_STAT
- REPLICATION_SLOTS
- GLOBAL_REPLICATION_SLOTS
- BGWRITER_STAT
- GLOBAL_BGWRITER_STAT
- GLOBAL_CKPT_STATUS
- GLOBAL_DOUBLE_WRITE_STATUS
- GLOBAL_PAGEWRITER_STATUS
- GLOBAL_RECORD_RESET_TIME
- GLOBAL_REDO_STATUS
- GLOBAL_RECOVERY_STATUS
- CLASS_VITAL_INFO
- USER_LOGIN
- SUMMARY_USER_LOGIN
- GLOBAL_GET_BGWRITER_STATUS
- GLOBAL_SINGLE_FLUSH_DW_STATUS
- GLOBAL_CANDIDATE_STATUS
- Lock
- Wait Events
- Configuration
- Operator
- Workload Manager
- Global Plancache
- RTO
- Appendix
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER Schema
- Overview
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.turn_on
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.turn_off
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.local_debug_server_info
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.attach
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.next
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.continue
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.abort
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.print_var
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.info_code
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.step
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.add_breakpoint
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.delete_breakpoint
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.info_breakpoints
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.backtrace
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.finish
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.set_var
- DB4AI Schema
- Tool Reference
- Tool Overview
- Client Tool
- Server Tools
- Tools Used in the Internal System
- gaussdb
- gs_backup
- gs_basebackup
- gs_ctl
- gs_initdb
- gs_install
- gs_install_plugin
- gs_install_plugin_local
- gs_postuninstall
- gs_preinstall
- gs_sshexkey
- gs_tar
- gs_uninstall
- gs_upgradectl
- gs_expansion
- gs_dropnode
- gs_probackup
- gstrace
- kdb5_util
- kadmin.local
- kinit
- klist
- krb5kdc
- kdestroy
- pg_config
- pg_controldata
- pg_recvlogical
- pg_resetxlog
- pg_archivecleanup
- pssh
- pscp
- transfer.py
- FAQ
- System Catalogs and Views Supported by gs_collector
- Extension Reference
- Error Code Reference
- Description of SQL Error Codes
- Third-Party Library Error Codes
- GAUSS-00001 - GAUSS-00100
- GAUSS-00101 - GAUSS-00200
- GAUSS 00201 - GAUSS 00300
- GAUSS 00301 - GAUSS 00400
- GAUSS 00401 - GAUSS 00500
- GAUSS 00501 - GAUSS 00600
- GAUSS 00601 - GAUSS 00700
- GAUSS 00701 - GAUSS 00800
- GAUSS 00801 - GAUSS 00900
- GAUSS 00901 - GAUSS 01000
- GAUSS 01001 - GAUSS 01100
- GAUSS 01101 - GAUSS 01200
- GAUSS 01201 - GAUSS 01300
- GAUSS 01301 - GAUSS 01400
- GAUSS 01401 - GAUSS 01500
- GAUSS 01501 - GAUSS 01600
- GAUSS 01601 - GAUSS 01700
- GAUSS 01701 - GAUSS 01800
- GAUSS 01801 - GAUSS 01900
- GAUSS 01901 - GAUSS 02000
- GAUSS 02001 - GAUSS 02100
- GAUSS 02101 - GAUSS 02200
- GAUSS 02201 - GAUSS 02300
- GAUSS 02301 - GAUSS 02400
- GAUSS 02401 - GAUSS 02500
- GAUSS 02501 - GAUSS 02600
- GAUSS 02601 - GAUSS 02700
- GAUSS 02701 - GAUSS 02800
- GAUSS 02801 - GAUSS 02900
- GAUSS 02901 - GAUSS 03000
- GAUSS 03001 - GAUSS 03100
- GAUSS 03101 - GAUSS 03200
- GAUSS 03201 - GAUSS 03300
- GAUSS 03301 - GAUSS 03400
- GAUSS 03401 - GAUSS 03500
- GAUSS 03501 - GAUSS 03600
- GAUSS 03601 - GAUSS 03700
- GAUSS 03701 - GAUSS 03800
- GAUSS 03801 - GAUSS 03900
- GAUSS 03901 - GAUSS 04000
- GAUSS 04001 - GAUSS 04100
- GAUSS 04101 - GAUSS 04200
- GAUSS 04201 - GAUSS 04300
- GAUSS 04301 - GAUSS 04400
- GAUSS 04401 - GAUSS 04500
- GAUSS 04501 - GAUSS 04600
- GAUSS 04601 - GAUSS 04700
- GAUSS 04701 - GAUSS 04800
- GAUSS 04801 - GAUSS 04900
- GAUSS 04901 - GAUSS 05000
- GAUSS 05001 - GAUSS 05100
- GAUSS 05101 - GAUSS 05200
- GAUSS 05201 - GAUSS 05300
- GAUSS 05301 - GAUSS 05400
- GAUSS 05401 - GAUSS 05500
- GAUSS 05501 - GAUSS 05600
- GAUSS 05601 - GAUSS 05700
- GAUSS 05701 - GAUSS 05800
- GAUSS 05801 - GAUSS 05900
- GAUSS 05901 - GAUSS 06000
- GAUSS 06001 - GAUSS 06100
- GAUSS 06101 - GAUSS 06200
- GAUSS 06201 - GAUSS 06300
- GAUSS 06301 - GAUSS 06400
- GAUSS 06401 - GAUSS 06500
- GAUSS 06501 - GAUSS 06600
- GAUSS 06601 - GAUSS 06700
- GAUSS 06701 - GAUSS 06800
- GAUSS 06801 - GAUSS 06900
- GAUSS 06901 - GAUSS 07000
- GAUSS 07001 - GAUSS 07100
- GAUSS 07101 - GAUSS 07200
- GAUSS 07201 - GAUSS 07300
- GAUSS 07301 - GAUSS 07400
- GAUSS 07401 - GAUSS 07480
- GAUSS 50000 - GAUSS 50999
- GAUSS 51000 - GAUSS 51999
- GAUSS 52000 - GAUSS 52999
- GAUSS 53000 - GAUSS 53699
- Error Log Reference
- System Catalogs and System Views
- Common Faults and Identification Guide
- Common Fault Locating Methods
- Common Fault Locating Cases
- Core Fault Locating
- Permission/Session/Data Type Fault Location
- Service/High Availability/Concurrency Fault Location
- Table/Partition Table Fault Location
- File System/Disk/Memory Fault Location
- After You Run the du Command to Query Data File Size In the XFS File System, the Query Result Is Greater than the Actual File Size
- File Is Damaged in the XFS File System
- Insufficient Memory
- "Error:No space left on device" Is Displayed
- When the TPC-C is running and a disk to be injected is full, the TPC-C stops responding
- Disk Space Usage Reaches the Threshold and the Database Becomes Read-only
- SQL Fault Location
- Index Fault Location
- Source Code Parsing
- FAQs
- Glossary
Hint-based Tuning
Plan Hint Optimization
In plan hints, you can specify a join order, join and scan operations, and the number of rows in a result to tune an execution plan, improving query performance.
Function
The hint syntax must follow immediately after a SELECT keyword and is written in the following format:
/*+ <plan hint>*/You can specify multiple hints for a query plan and separate them by spaces. A hint specified for a query plan does not apply to its subquery plans. To specify a hint for a subquery, add the hint following the SELECT of this subquery.
For example:
select /*+ <plan_hint1> <plan_hint2> */ * from t1, (select /*+ <plan_hint3> */ from t2) where 1=1;In the preceding command, <plan_hint1> and <plan_hint2> are the hints of a query, and <plan_hint3> is the hint of its subquery.
NOTICE: If a hint is specified in the CREATE VIEW statement, the hint will be applied each time this view is used. If the random plan function is enabled (plan_mode_seed is set to a value other than 0), the specified hint will not be used.
Scope
Currently, the following hints are supported:
- Join order hints (leading)
- Join operation hints, excluding the semi join, anti join, and unique plan hints
- Rows hints
- Scan operation hints, supporting only tablescan, indexscan, and indexonlyscan
- Sublink name hints
Precautions
Hints do not support Agg, Sort, Setop, or Subplan.
Example
The following is the original plan and is used for comparing with the optimized ones:
create table store
(
s_store_sk integer not null,
s_store_id char(16) not null,
s_rec_start_date date ,
s_rec_end_date date ,
s_closed_date_sk integer ,
s_store_name varchar(50) ,
s_number_employees integer ,
s_floor_space integer ,
s_hours char(20) ,
s_manager varchar(40) ,
s_market_id integer ,
s_geography_class varchar(100) ,
s_market_desc varchar(100) ,
s_market_manager varchar(40) ,
s_division_id integer ,
s_division_name varchar(50) ,
s_company_id integer ,
s_company_name varchar(50) ,
s_street_number varchar(10) ,
s_street_name varchar(60) ,
s_street_type char(15) ,
s_suite_number char(10) ,
s_city varchar(60) ,
s_county varchar(30) ,
s_state char(2) ,
s_zip char(10) ,
s_country varchar(20) ,
s_gmt_offset decimal(5,2) ,
s_tax_precentage decimal(5,2) ,
primary key (s_store_sk)
);
create table store_sales
(
ss_sold_date_sk integer ,
ss_sold_time_sk integer ,
ss_item_sk integer not null,
ss_customer_sk integer ,
ss_cdemo_sk integer ,
ss_hdemo_sk integer ,
ss_addr_sk integer ,
ss_store_sk integer ,
ss_promo_sk integer ,
ss_ticket_number integer not null,
ss_quantity integer ,
ss_wholesale_cost decimal(7,2) ,
ss_list_price decimal(7,2) ,
ss_sales_price decimal(7,2) ,
ss_ext_discount_amt decimal(7,2) ,
ss_ext_sales_price decimal(7,2) ,
ss_ext_wholesale_cost decimal(7,2) ,
ss_ext_list_price decimal(7,2) ,
ss_ext_tax decimal(7,2) ,
ss_coupon_amt decimal(7,2) ,
ss_net_paid decimal(7,2) ,
ss_net_paid_inc_tax decimal(7,2) ,
ss_net_profit decimal(7,2) ,
primary key (ss_item_sk, ss_ticket_number)
);
create table store_returns
(
sr_returned_date_sk integer ,
sr_return_time_sk integer ,
sr_item_sk integer not null,
sr_customer_sk integer ,
sr_cdemo_sk integer ,
sr_hdemo_sk integer ,
sr_addr_sk integer ,
sr_store_sk integer ,
sr_reason_sk integer ,
sr_ticket_number integer not null,
sr_return_quantity integer ,
sr_return_amt decimal(7,2) ,
sr_return_tax decimal(7,2) ,
sr_return_amt_inc_tax decimal(7,2) ,
sr_fee decimal(7,2) ,
sr_return_ship_cost decimal(7,2) ,
sr_refunded_cash decimal(7,2) ,
sr_reversed_charge decimal(7,2) ,
sr_store_credit decimal(7,2) ,
sr_net_loss decimal(7,2) ,
primary key (sr_item_sk, sr_ticket_number)
);
create table customer
(
c_customer_sk integer not null,
c_customer_id char(16) not null,
c_current_cdemo_sk integer ,
c_current_hdemo_sk integer ,
c_current_addr_sk integer ,
c_first_shipto_date_sk integer ,
c_first_sales_date_sk integer ,
c_salutation char(10) ,
c_first_name char(20) ,
c_last_name char(30) ,
c_preferred_cust_flag char(1) ,
c_birth_day integer ,
c_birth_month integer ,
c_birth_year integer ,
c_birth_country varchar(20) ,
c_login char(13) ,
c_email_address char(50) ,
c_last_review_date char(10) ,
primary key (c_customer_sk)
);
create table promotion
(
p_promo_sk integer not null,
p_promo_id char(16) not null,
p_start_date_sk integer ,
p_end_date_sk integer ,
p_item_sk integer ,
p_cost decimal(15,2) ,
p_response_target integer ,
p_promo_name char(50) ,
p_channel_dmail char(1) ,
p_channel_email char(1) ,
p_channel_catalog char(1) ,
p_channel_tv char(1) ,
p_channel_radio char(1) ,
p_channel_press char(1) ,
p_channel_event char(1) ,
p_channel_demo char(1) ,
p_channel_details varchar(100) ,
p_purpose char(15) ,
p_discount_active char(1) ,
primary key (p_promo_sk)
);
create table customer_address
(
ca_address_sk integer not null,
ca_address_id char(16) not null,
ca_street_number char(10) ,
ca_street_name varchar(60) ,
ca_street_type char(15) ,
ca_suite_number char(10) ,
ca_city varchar(60) ,
ca_county varchar(30) ,
ca_state char(2) ,
ca_zip char(10) ,
ca_country varchar(20) ,
ca_gmt_offset decimal(5,2) ,
ca_location_type char(20) ,
primary key (ca_address_sk)
);
create table item
(
i_item_sk integer not null,
i_item_id char(16) not null,
i_rec_start_date date ,
i_rec_end_date date ,
i_item_desc varchar(200) ,
i_current_price decimal(7,2) ,
i_wholesale_cost decimal(7,2) ,
i_brand_id integer ,
i_brand char(50) ,
i_class_id integer ,
i_class char(50) ,
i_category_id integer ,
i_category char(50) ,
i_manufact_id integer ,
i_manufact char(50) ,
i_size char(20) ,
i_formulation char(20) ,
i_color char(20) ,
i_units char(10) ,
i_container char(10) ,
i_manager_id integer ,
i_product_name char(50) ,
primary key (i_item_sk)
);
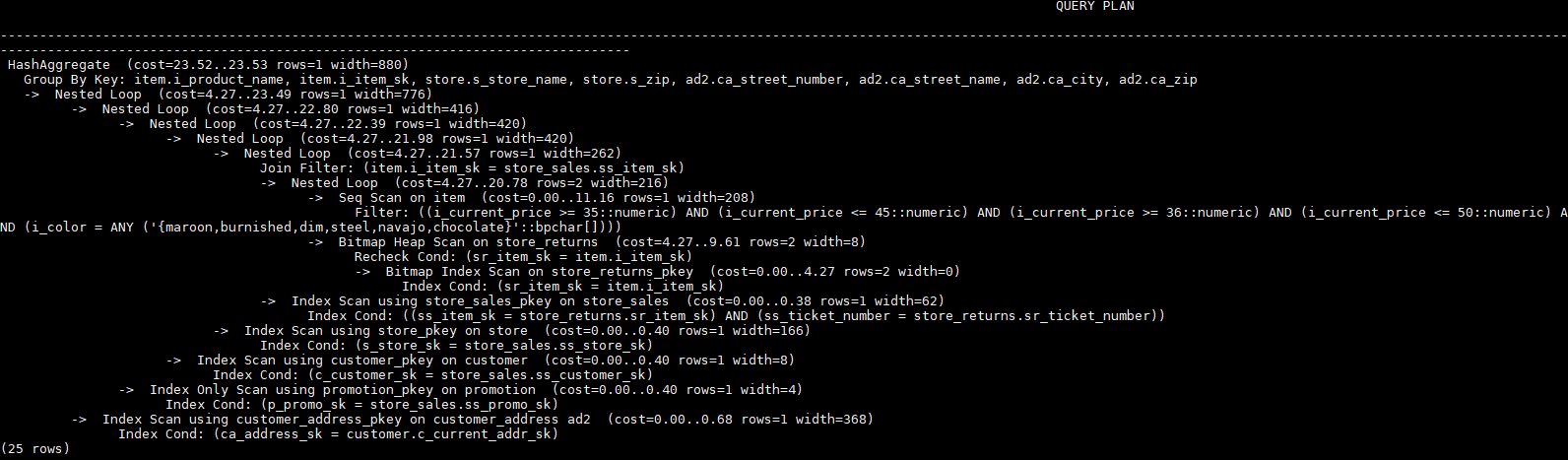
explain
select i_product_name product_name
,i_item_sk item_sk
,s_store_name store_name
,s_zip store_zip
,ad2.ca_street_number c_street_number
,ad2.ca_street_name c_street_name
,ad2.ca_city c_city
,ad2.ca_zip c_zip
,count(*) cnt
,sum(ss_wholesale_cost) s1
,sum(ss_list_price) s2
,sum(ss_coupon_amt) s3
FROM store_sales
,store_returns
,store
,customer
,promotion
,customer_address ad2
,item
WHERE ss_store_sk = s_store_sk AND
ss_customer_sk = c_customer_sk AND
ss_item_sk = i_item_sk and
ss_item_sk = sr_item_sk and
ss_ticket_number = sr_ticket_number and
c_current_addr_sk = ad2.ca_address_sk and
ss_promo_sk = p_promo_sk and
i_color in ('maroon','burnished','dim','steel','navajo','chocolate') and
i_current_price between 35 and 35 + 10 and
i_current_price between 35 + 1 and 35 + 15
group by i_product_name
,i_item_sk
,s_store_name
,s_zip
,ad2.ca_street_number
,ad2.ca_street_name
,ad2.ca_city
,ad2.ca_zip
;
Join Order Hints
Function
Theses hints specify the join order and outer/inner tables.
Syntax
-
Specify only the join order.
leading(join_table_list) -
Specify the join order and outer/inner tables. The outer/inner tables are specified by the outermost parentheses.
leading((join_table_list))
Parameter Description
join_table_list specifies the tables to be joined. The values can be table names or table aliases. If a subquery is pulled up, the value can also be the subquery alias. Separate the values with spaces. You can add parentheses to specify the join priorities of tables.
NOTICE: A table name or alias can only be a string without a schema name. An alias (if any) is used to represent a table.
To prevent semantic errors, tables in the list must meet the following requirements:
- The tables must exist in the query or its subquery to be pulled up.
- The table names must be unique in the query or subquery to be pulled up. If they are not, their aliases must be unique.
- A table appears only once in the list.
- An alias (if any) is used to represent a table.
For example:
leading(t1 t2 t3 t4 t5):t1, t2, t3, t4, and t5 are joined. The join order and outer/inner tables are not specified.
leading((t1 t2 t3 t4 t5)):t1, t2, t3, t4, and t5 are joined in sequence. The table on the right is used as the inner table in each join.
leading(t1 (t2 t3 t4) t5): First, t2, t3, and t4 are joined and the outer/inner tables are not specified. Then, the result is joined with t1 and t5, and the outer/inner tables are not specified.
leading((t1 (t2 t3 t4) t5)): First, t2, t3, and t4 are joined and the outer/inner tables are not specified. Then, the result is joined with t1, and (t2 t3 t4) is used as the inner table. Finally, the result is joined with t5, and t5 is used as the inner table.
leading((t1 (t2 t3) t4 t5)) leading((t3 t2)): First, t2 and t3 are joined and t2 is used as the inner table. Then, the result is joined with t1, and (t2 t3) is used as the inner table. Finally, the result is joined with t4 and then t5, and the table on the right in each join is used as the inner table.
Example
Hint the query plan in Example as follows:
explain
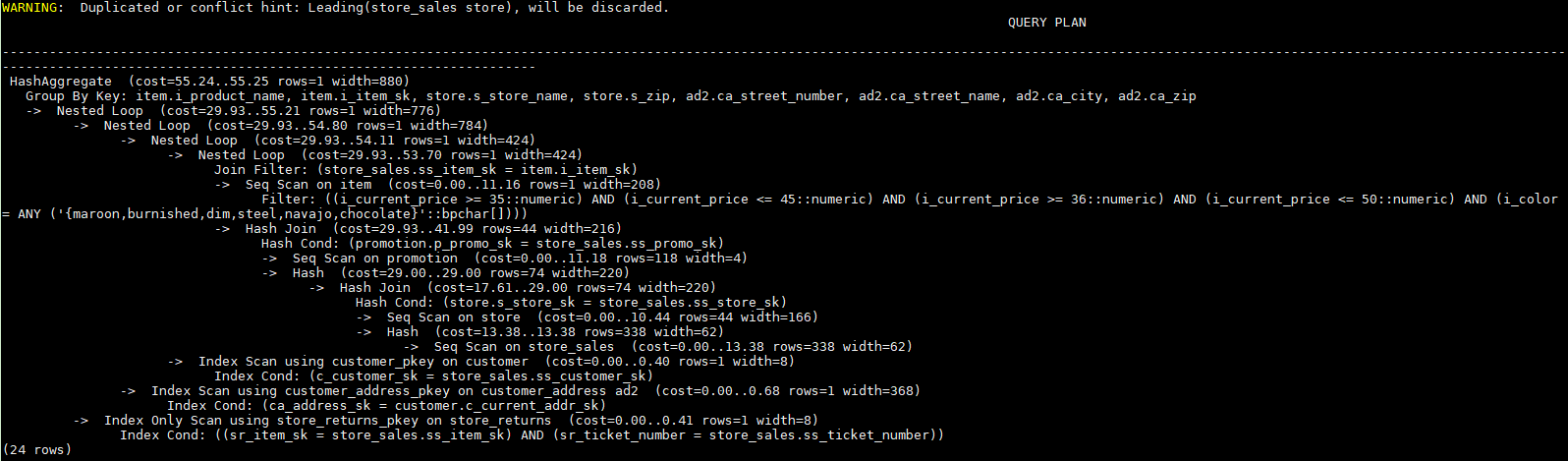
select /*+ leading((((((store_sales store) promotion) item) customer) ad2) store_returns) leading((store store_sales))*/ i_product_name product_name ...First, store_sales and store are joined and store_sales is the inner table. Then, the result is joined with promotion, item, customer, ad2, and store_returns in sequence. The optimized plan is as follows:
Join Operation Hints
Function
These hints specify the join method, which can be nested loop join, hash join, or merge join.
Syntax
[no] nestloop|hashjoin|mergejoin(table_list)Parameter Description
- no indicates that the specified hint will not be used for a join.
- table_list specifies the tables to be joined. The values are the same as those of join_table_list but contain no parentheses.
For example:
no nestloop(t1 t2 t3):nestloop is not used for joining t1, t2, and t3. The three tables may be joined in either of the two ways: Join t2 and t3, and then t1; join t1 and t2, and then t3. This hint takes effect only for the last join. If necessary, you can hint other joins. For example, you can add no nestloop(t2 t3) to join t2 and t3 first and to forbid the use of nestloop.
Example
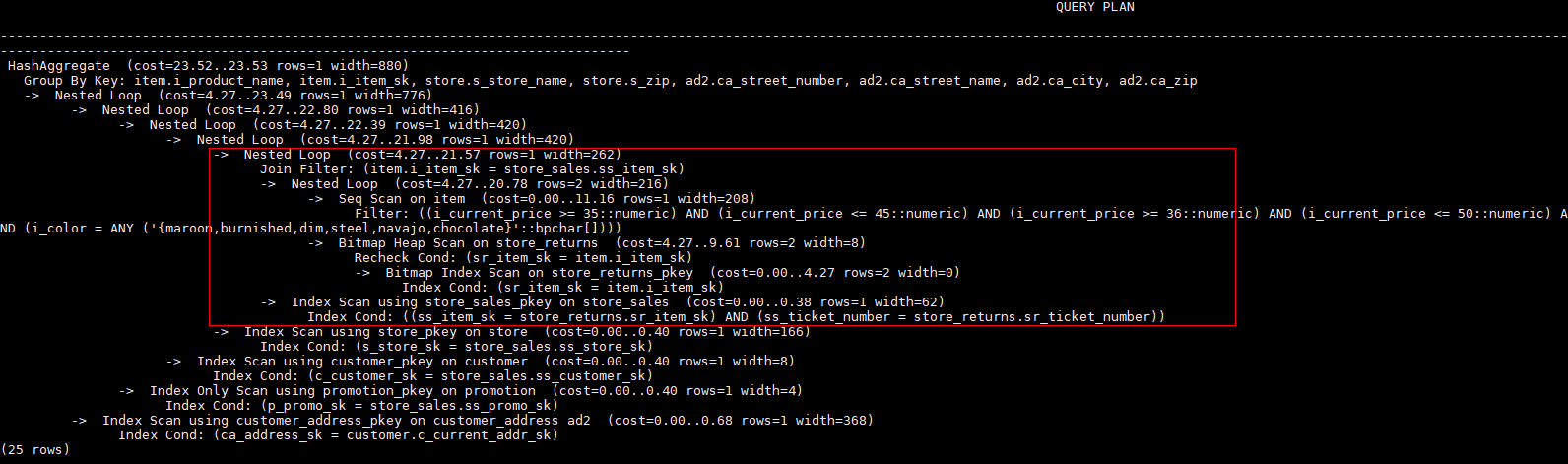
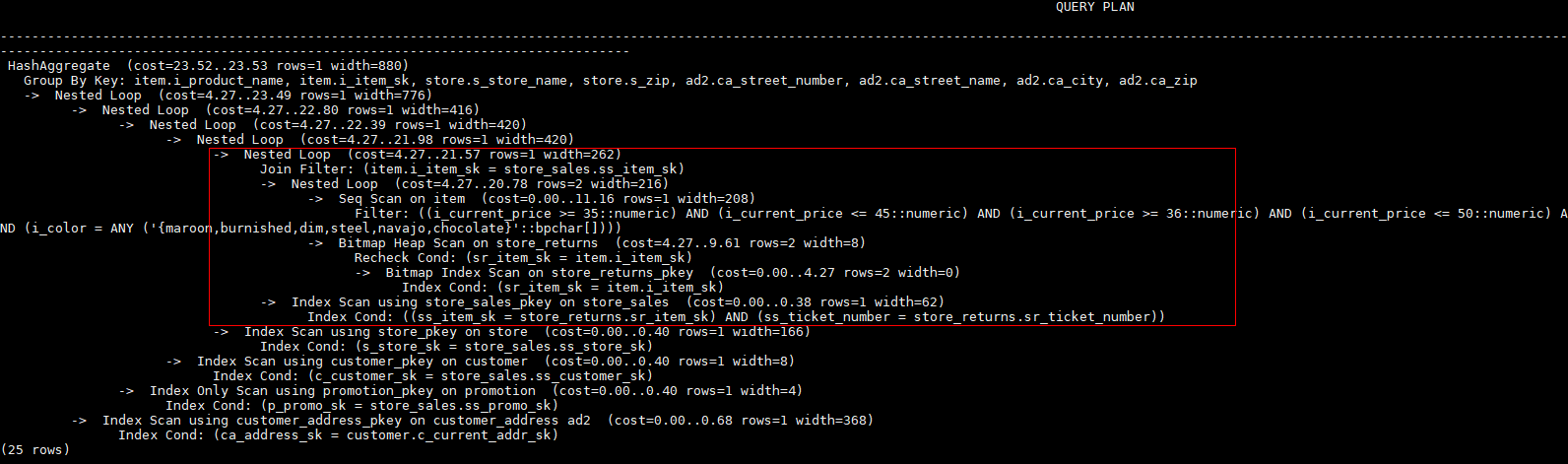
Hint the query plan in Example as follows:
explain
select /*+ nestloop(store_sales store_returns item) */ i_product_name product_name ...nestloop is used for the last join between store_sales, store_returns, and item. The optimized plan is as follows:
Rows Hints
Function
These hints specify the number of rows in an intermediate result set. Both absolute values and relative values are supported.
Syntax
rows(table_list #|+|-|* const)Parameter Description
- #, +, -, and * are operators used for hinting the estimation. # indicates that the original estimation is used without any calculation. +, -, and * indicate that the original estimation is calculated using these operators. The minimum calculation result is 1. table_list specifies the tables to be joined. The values are the same as those of table_list in Join Operation Hints.
- const can be any non-negative number and supports scientific notation.
For example:
rows(t1 #5): The result set of t1 is five rows.
rows(t1 t2 t3 *1000): Multiply the result set of joined t1, t2, and t3 by 1000.
Suggestion
- The hint using * for two tables is recommended. This hint will be triggered if the two tables appear on two sides of a join. For example, if the hint is rows(t1 t2 * 3), the join result of (t1 t3 t4) and (t2 t5 t6) will be multiplied by 3 because t1 and t2 appear on both sides of the join.
- rows hints can be specified for the result sets of a single table, multiple tables, function tables, and subquery scan tables.
Example
Hint the query plan in Example as follows:
explain
select /*+ rows(store_sales store_returns *50) */ i_product_name product_name ...Multiply the result set of joined store_sales and store_returns by 50. The optimized plan is as follows:
Scan Operation Hints
Function
These hints specify a scan operation, which can be tablescan, indexscan, or indexonlyscan.
Syntax
[no] tablescan|indexscan|indexonlyscan(table [index])Parameter Description
- no indicates that the specified hint will not be used for a join.
- table specifies the table to be scanned. You can specify only one table. Use a table alias (if any) instead of a table name.
- index indicates the index for indexscan or indexonlyscan. You can specify only one index.
NOTE: indexscan and indexonlyscan hints can be used only when the specified index belongs to the table. Scan operation hints can be used for row-store tables, column-store tables, OBS tables, and subquery tables.
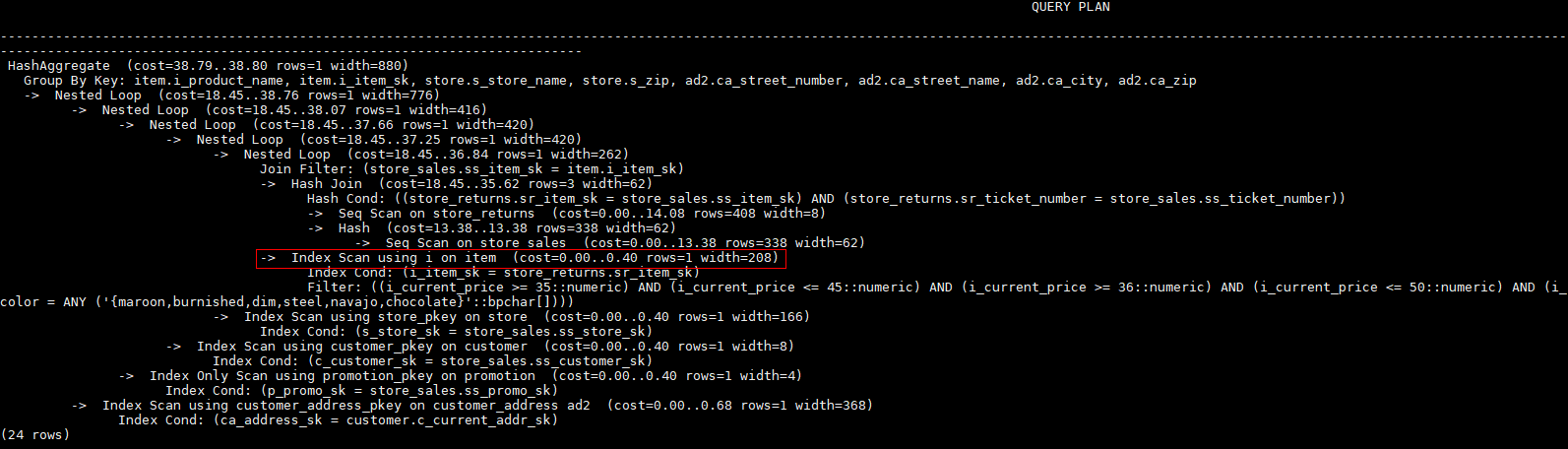
Example
To specify an index-based hint for a scan, create an index named i on the i_item_sk column of the item table.
create index i on item(i_item_sk);Hint the query plan in Example as follows:
explain
select /*+ indexscan(item i) */ i_product_name product_name ...item is scanned based on an index. The optimized plan is as follows:
Sublink Name Hints
Function
These hints specify the name of a sublink block.
Syntax
blockname (table)Parameter Description
- table specifies the name you have specified for a sublink block.
NOTE:
- The blockname hint is used by an outer query only when a sublink is pulled up. Currently, only the Agg equivalent join, IN, and EXISTS sublinks can be pulled up. This hint is usually used together with the hints described in the previous sections.
- The subquery after the FROM keyword is hinted by using the subquery alias. In this case, blockname becomes invalid.
- If a sublink contains multiple tables, the tables will be joined with the outer-query tables in a random sequence after the sublink is pulled up. In this case, blockname also becomes invalid.
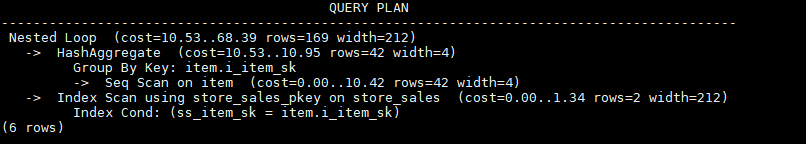
Example
explain select /*+nestloop(store_sales tt) */ * from store_sales where ss_item_sk in (select /*+blockname(tt)*/ i_item_sk from item group by 1);tt indicates the sublink block name. After being pulled up, the sublink is joined with the outer-query table store_sales by using nestloop. The optimized plan is as follows:
Hint Errors, Conflicts, and Other Warnings
Plan hints change an execution plan. You can run EXPLAIN to view the changes.
Hints containing errors are invalid and do not affect statement execution. The errors will be displayed in different ways based on statement types. Hint errors in an EXPLAIN statement are displayed as a warning on the interface. Hint errors in other statements will be recorded in debug1-level logs containing the PLANHINT keyword.
Hint error types are as follows:
-
Syntax errors
An error will be reported if the syntax tree fails to be reduced. The No. of the row generating an error is displayed in the error details.
For example, the hint keyword is incorrect, no table or only one table is specified in the leading or join hint, or no tables are specified in other hints. The parsing of a hint is terminated immediately after a syntax error is detected. Only the hints that have been parsed successfully are valid.
For example:
leading((t1 t2)) nestloop(t1) rows(t1 t2 #10)The syntax of nestloop(t1) is wrong and its parsing is terminated. Only leading(t1 t2) that has been successfully parsed before nestloop(t1) is valid.
-
Semantic errors
- An error will be reported if the specified tables do not exist, multiple tables are found based on the hint setting, or a table is used more than once in the leading or join hint.
- An error will be reported if the index specified in a scan hint does not exist.
- If multiple tables with the same name exist after a subquery is pulled up and some of them need to be hinted, add aliases for them to avoid name duplication.
-
Duplicated or conflicted hints
If hint duplication or conflicts occur, only the first hint takes effect. A message will be displayed to describe the situation.
-
Hint duplication indicates that a hint is used more than once in the same query, for example, nestloop(t1 t2) nestloop(t1 t2).
-
A hint conflict indicates that the functions of two hints with the same table list conflict with each other.
For example, if nestloop (t1 t2) hashjoin (t1 t2) is used, hashjoin (t1 t2) becomes invalid. nestloop(t1 t2) does not conflict with no mergejoin(t1 t2).
 NOTICE:
The table list in the leading hint is disassembled. For example, leading ((t1 t2 t3)) will be disassembled as leading((t1 t2)) leading(((t1 t2) t3)), which will conflict with leading((t2 t1)) (if any). In this case, the latter leading(t2 t1) becomes invalid. If two hints use duplicated table lists and only one of them has the specified outer/inner table, the one without a specified outer/inner table becomes invalid.
NOTICE:
The table list in the leading hint is disassembled. For example, leading ((t1 t2 t3)) will be disassembled as leading((t1 t2)) leading(((t1 t2) t3)), which will conflict with leading((t2 t1)) (if any). In this case, the latter leading(t2 t1) becomes invalid. If two hints use duplicated table lists and only one of them has the specified outer/inner table, the one without a specified outer/inner table becomes invalid.
-
-
A hint becomes invalid after a sublink is pulled up.
In this case, a message will be displayed. Generally, such invalidation occurs when a sublink contains multiple tables to be joined. After the sublink is pulled up, the tables will not be join members.
-
Unsupported column types
- Skew hints are specified to optimize redistribution. They will be invalid if their corresponding columns do not support redistribution.
-
Hints are not used.
- If hashjoin or mergejoin is specified for non-equivalent joins, it will not be used.
- If indexscan or indexonlyscan is specified for a table that does not have an index, it will not be used.
- If indexscan hint or indexonlyscan is specified for a full-table scan or for a scan whose filtering conditions are not set on index columns, it will not be used.
- The specified indexonlyscan hint is used only when the output column contains only indexes.
- In equivalent joins, only the joins containing equivalence conditions are valid. Therefore, the leading, join, and rows hints specified for the joins without an equivalence condition will not be used. For example, t1, t2, and t3 are to be joined, and the join between t1 and t3 does not contain an equivalence condition. In this case, leading(t1 t3) will not be used.
- To generate a streaming plan, if the distribution key of a table is the same as its join key, redistribute specified for this table will not be used. If the distribution key and join key are different for this table but the same for the other table in the join, redistribute specified for this table will be used but broadcast will not.
- If no sublink is pulled up, the specified blockname hint will not be used.
- Skew hints are not used possibly because:
- The plan does not require redistribution.
- The columns specified by hints contain distribution keys.
- Skew information specified in hints is incorrect or incomplete, for example, no value is specified for join optimization.
- Skew optimization is disabled by GUC parameters.
Optimizer GUC Parameter Hints
Function
Sets GUC parameters related to query optimization that take effect during the query execution. For details about the application scenarios of hints, see the description of each GUC parameter.
Syntax
set(param value)Parameters
-
param indicates the parameter name.
-
value indicates the value of a parameter.
-
Currently, the following parameters can be set and take effect by using Hint:
-
Boolean
- enable_bitmapscan
- enable_hashagg
- enable_hashjoin
- enable_indexscan
- enable_indexonlyscan
- enable_material
- enable_mergejoin
- enable_nestloop
- enable_index_nestloop
- enable_seqscan
- enable_sort
- enable_tidscan
-
Integer
query_dop
-
Floating point
- cost_weight_index
- default_limit_rows
- seq_page_cost
- random_page_cost
- cpu_tuple_cost
- cpu_index_tuple_cost
- cpu_operator_cost
- effective_cache_size
-
NOTE:
- If you set a parameter that is not in the whitelist and the parameter value is invalid or the hint syntax is incorrect, the query execution is not affected. Run explain(verbose on). An error message is displayed, indicating that hint parsing fails.
- The GUC parameter hint takes effect only in the outermost query. That is, the GUC parameter hint in the subquery does not take effect.
- The GUC parameter hint in the view definition does not take effect.
- In the CREATE TABLE ... AS ... statement, the outermost GUC parameter hint takes effect.
Hint for Selecting the Custom Plan or Generic Plan
Function
For query statements and DML statements executed in PBE mode, the optimizer generates a custom plan or generic plan based on factors such as rules, costs, and parameters. You can use the hint of use_cplan or use_gplan to specify the plan to execute.
Syntax
-
To select the custom plan, run the following statement:
use_cplan -
To select the generic plan, run the following statement:
use_gplan
NOTE:
- For SQL statements that are executed in non-PBE mode, setting this hint does not affect the execution mode.
- This hint has a higher priority than cost-based selection and the plan_cache_mode parameter. That is, this hint does not take effect for statements for which plan_cache_mode cannot be forcibly set to specify an execution mode.
Examples
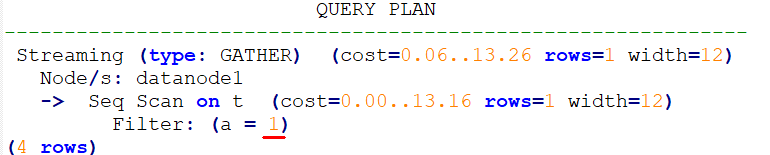
Forcibly use the custom plan.
set enable_fast_query_shipping = off;
create table t (a int, b int, c int);
prepare p as select /*+ use_cplan */ * from t where a = $1;
explain execute p(1);In the following plan, the filtering condition is the actual value of the input parameter, that is, the plan is a custom plan.
Forcibly use the generic plan.
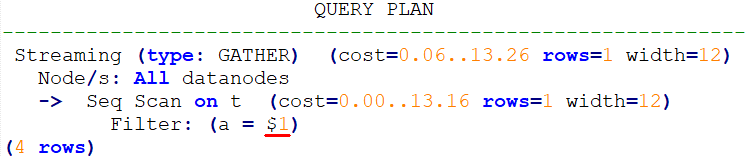
deallocate p;
prepare p as select /*+ use_gplan */ * from t where a = $1;
explain execute p(1);In the following plan, the filtering condition is the input parameter to be added, that is, the plan is a custom plan.
Hint Specifying Not to Expand Subqueries
Function
When the database optimizes the query logic, some subqueries can be promoted to the upper layer to avoid nested execution. However, for some subqueries that have a low selection rate and can use indexes to filter access pages, nested execution does not cause too much performance deterioration, while after the promotion, the query search scope is expanded, which may cause performance deterioration. In this case, you can use the no_expand hint for debugging. This hint is not recommended in most cases.
Syntax
no_expandExamples
Normal query execution:
explain select * from t1 where t1.a in (select t2.a from t2);Plan:
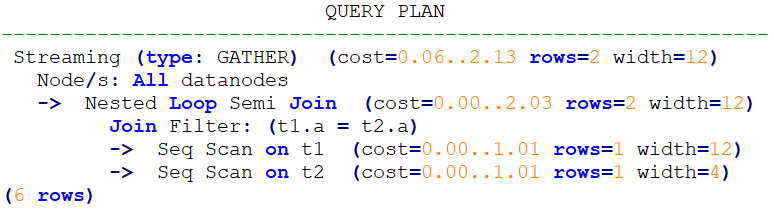
After no_expand is added:
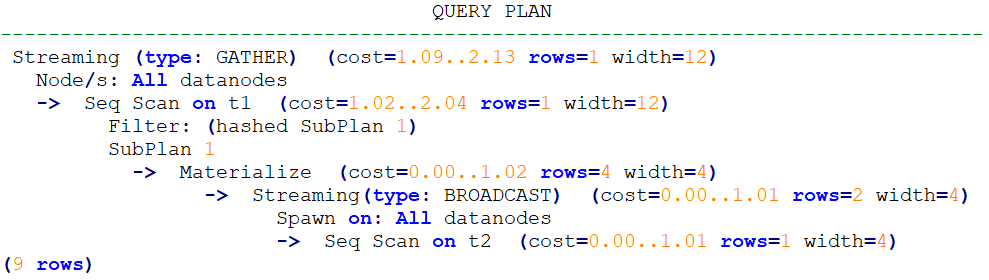
explain select * from t1 where t1.a in (select /*+ no_expand*/ t2.a from t2);Plan:
Hint Specifying Not to Use Global Plan Cache
Function
When global plan cache is enabled, you can use the no_gpc hint to force a single query statement not to share the plan cache globally. Only the plan cache within the current session lifecycle is retained.
Syntax
no_gpc
NOTE: This parameter takes effect only for statements executed by PBE when enable_global_plancache is set to on.
Example
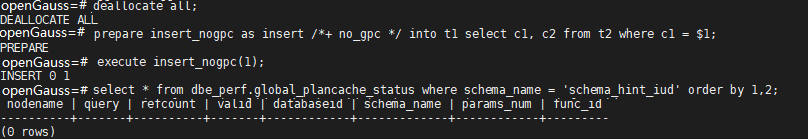
No result exists in the dbe_perf.global_plancache_status view, that is, no plan is cached globally.