- 关于MogDB
- 快速入门
- 特性描述
- 概览
- 高性能
- 高可用
- 维护性
- 兼容性
- 视图增加%rowtype属性
- 聚合函数distinct性能优化
- 聚合函数支持KEEP子句
- 聚合函数支持场景扩展
- 兼容支持MySQL别名支持单引号
- 支持current_date/current_time关键字作为字段名
- 自定义type数组
- For Update支持外连接
- MogDB支持Insert All特性
- Oracle DBLink语法兼容
- 创建PACKAGE/FUNCTION/PROCEDURE时去除TYPE类型转换提示
- 支持MERGE INTO命中索引时使用Bypass方法
- 支持增加存储过程及函数参数的nocopy属性
- 支持在数组extend的参数中传入数组的count属性
- 支持q quote转义字符
- 支持两个date类型的数据相减返回numeric类型
- 支持表函数table()
- 支持PROCEDURE/FUNCTION/PACKAGE的end后的name和Oracle保持一致
- 支持WHERE CURRENT OF写法
- 支持包内常量作为函数或者过程入参的默认值
- 支持PLPGSQL subtype
- 支持无参数FUNCTION的同义词调用不加括号
- 支持dbms_utility.format_error_backtrace
- 支持PIVOT和UNPIVOT语法
- mod函数兼容
- 支持聚集函数嵌套
- ORDER BY/GROUP BY场景兼容
- 支持在建表后修改表日志属性
- INSERT支持ON CONFLICT子句
- 支持AUTHID CURRENT_USER
- PBE模式支持存储过程out出参
- 数据库安全
- 企业级特性
- 应用开发接口
- AI能力
- 中间件
- 负载管理
- 安装指南
- 升级指南
- 管理指南
- 高可用指南
- AI特性指南
- 安全指南
- 开发者指南
- 应用程序开发教程
- 开发规范
- 基于JDBC开发
- JDBC包、驱动类和环境类
- 开发流程
- 加载驱动
- 连接数据库
- 连接数据库(以SSL方式)
- 连接数据库(UDS方式)
- 执行SQL语句
- 处理结果集
- 关闭连接
- 日志管理
- 示例:常用操作
- 示例:重新执行应用SQL
- 示例:通过本地文件导入导出数据
- 示例:从MY向MogDB进行数据迁移
- 示例:逻辑复制代码示例
- 示例:不同场景下连接数据库参数配置
- 示例:jdbc主备集群负载均衡
- JDBC接口参考
- java.sql.Connection
- java.sql.CallableStatement
- java.sql.DatabaseMetaData
- java.sql.Driver
- java.sql.PreparedStatement
- java.sql.ResultSet
- java.sql.ResultSetMetaData
- java.sql.Statement
- javax.sql.ConnectionPoolDataSource
- javax.sql.DataSource
- javax.sql.PooledConnection
- javax.naming.Context
- javax.naming.spi.InitialContextFactory
- CopyManager
- JDBC常用参数参考
- JDBC发布记录
- 基于ODBC开发
- 基于libpq开发
- 基于Psycopg2开发
- 基于.NET开发
- 基于MogOCI开发
- 调试
- 存储过程
- 用户自定义函数
- PL/pgSQL-SQL过程语言
- 定时任务
- 自治事务
- 逻辑复制
- Extension
- MySQL兼容性说明
- Dolphin Extension
- Dolphin概述
- Dolphin安装
- Dolphin限制
- Dolphin语法介绍
- SQL参考
- 关键字
- 数据类型
- 函数和操作符
- 表达式
- DDL语法一览表
- DML语法一览表
- DCL语法一览表
- SQL语法
- ALTER DATABASE
- ALTER FUNCTION
- ALTER PROCEDURE
- ALTER SERVER
- ALTER TABLE
- ALTER TABLE PARTITION
- ALTER TABLESPACE
- ALTER VIEW
- ANALYZE | ANALYSE
- AST
- CHECKSUM TABLE
- CREATE DATABASE
- CREATE FUNCTION
- CREATE INDEX
- CREATE PROCEDURE
- CREATE SERVER
- CREATE TABLE
- CREATE TABLE AS
- CREATE TABLE PARTITION
- CREATE TABLESPACE
- CREATE TRIGGER
- CREATE VIEW
- DESCRIBE TABLE
- DO
- DROP DATABASE
- DROP INDEX
- DROP TABLESPACE
- EXECUTE
- EXPLAIN
- FLUSH BINARY LOGS
- GRANT
- GRANT/REVOKE PROXY
- INSERT
- KILL
- LOAD DATA
- OPTIMIZE TABLE
- PREPARE
- RENAME TABLE
- RENAME USER
- REVOKE
- SELECT
- SELECT HINT
- SET CHARSET
- SET PASSWORD
- SHOW CHARACTER SET
- SHOW COLLATION
- SHOW COLUMNS
- SHOW CREATE DATABASE
- SHOW CREATE FUNCTION
- SHOW CREATE PROCEDURE
- SHOW CREATE TABLE
- SHOW CREATE TRIGGER
- SHOW CREATE VIEW
- SHOW DATABASES
- SHOW FUNCTION STATUS
- SHOW GRANTS
- SHOW INDEX
- SHOW MASTER STATUS
- SHOW PLUGINS
- SHOW PRIVILEGES
- SHOW PROCEDURE STATUS
- SHOW PROCESSLIST
- SHOW SLAVE HOSTS
- SHOW STATUS
- SHOW TABLES
- SHOW TABLE STATUS
- SHOW TRIGGERS
- SHOW VARIABLES
- SHOW WARNINGS/ERRORS
- UPDATE
- USE db_name
- 系统视图
- GUC参数说明
- 重设参数
- 存储过程
- 标识符说明
- SQL参考
- MySQL语法兼容性评估工具
- Dolphin Extension
- 物化视图
- 分区管理
- 应用程序开发教程
- 性能优化指南
- 参考指南
- 系统表及系统视图
- 系统表和系统视图概述
- 查看系统表
- 系统表
- GS_ASP
- GS_AUDITING_POLICY
- GS_AUDITING_POLICY_ACCESS
- GS_AUDITING_POLICY_FILTERS
- GS_AUDITING_POLICY_PRIVILEGES
- GS_CLIENT_GLOBAL_KEYS
- GS_CLIENT_GLOBAL_KEYS_ARGS
- GS_COLUMN_KEYS
- GS_COLUMN_KEYS_ARGS
- GS_DB_PRIVILEGE
- GS_ENCRYPTED_COLUMNS
- GS_ENCRYPTED_PROC
- GS_GLOBAL_CHAIN
- GS_GLOBAL_CONFIG
- GS_MASKING_POLICY
- GS_MASKING_POLICY_ACTIONS
- GS_MASKING_POLICY_FILTERS
- GS_MATVIEW
- GS_MATVIEW_DEPENDENCY
- GS_MODEL_WAREHOUSE
- GS_OPT_MODEL
- GS_PACKAGE
- GS_POLICY_LABEL
- GS_RECYCLEBIN
- GS_TXN_SNAPSHOT
- GS_UID
- GS_WLM_EC_OPERATOR_INFO
- GS_WLM_INSTANCE_HISTORY
- GS_WLM_OPERATOR_INFO
- GS_WLM_PLAN_ENCODING_TABLE
- GS_WLM_PLAN_OPERATOR_INFO
- GS_WLM_SESSION_QUERY_INFO_ALL
- GS_WLM_USER_RESOURCE_HISTORY
- PG_AGGREGATE
- PG_AM
- PG_AMOP
- PG_AMPROC
- PG_APP_WORKLOADGROUP_MAPPING
- PG_ATTRDEF
- PG_ATTRIBUTE
- PG_AUTH_HISTORY
- PG_AUTH_MEMBERS
- PG_AUTHID
- PG_CAST
- PG_CLASS
- PG_COLLATION
- PG_CONSTRAINT
- PG_CONVERSION
- PG_DATABASE
- PG_DB_ROLE_SETTING
- PG_DEFAULT_ACL
- PG_DEPEND
- PG_DESCRIPTION
- PG_DIRECTORY
- PG_ENUM
- PG_EVENT_TRIGGER
- PG_EXTENSION
- PG_EXTENSION_DATA_SOURCE
- PG_FOREIGN_DATA_WRAPPER
- PG_FOREIGN_SERVER
- PG_FOREIGN_TABLE
- PG_HASHBUCKET
- PG_INDEX
- PG_INHERITS
- PG_JOB
- PG_JOB_PROC
- PG_LANGUAGE
- PG_LARGEOBJECT
- PG_LARGEOBJECT_METADATA
- PG_NAMESPACE
- PG_OBJECT
- PG_OPCLASS
- PG_OPERATOR
- PG_OPFAMILY
- PG_PARTITION
- PG_PLTEMPLATE
- PG_PROC
- PG_PUBLICATION
- PG_PUBLICATION_REL
- PG_RANGE
- PG_REPLICATION_ORIGIN
- PG_RESOURCE_POOL
- PG_REWRITE
- PG_RLSPOLICY
- PG_SECLABEL
- PG_SET
- PG_SHDEPEND
- PG_SHDESCRIPTION
- PG_SHSECLABEL
- PG_STATISTIC
- PG_STATISTIC_EXT
- PG_SUBSCRIPTION
- PG_SUBSCRIPTION_REL
- PG_SYNONYM
- PG_TABLESPACE
- PG_TRIGGER
- PG_TS_CONFIG
- PG_TS_CONFIG_MAP
- PG_TS_DICT
- PG_TS_PARSER
- PG_TS_TEMPLATE
- PG_TYPE
- PG_USER_MAPPING
- PG_USER_STATUS
- PG_WORKLOAD_GROUP
- PGXC_CLASS
- PGXC_GROUP
- PGXC_NODE
- PGXC_SLICE
- PLAN_TABLE_DATA
- STATEMENT_HISTORY
- 系统视图
- GET_GLOBAL_PREPARED_XACTS(废弃)
- GS_ASYNC_SUBMIT_SESSIONS_STATUS
- GS_AUDITING
- GS_AUDITING_ACCESS
- GS_AUDITING_PRIVILEGE
- GS_CLUSTER_RESOURCE_INFO
- GS_COMPRESSION
- GS_DB_PRIVILEGES
- GS_FILE_STAT
- GS_GSC_MEMORY_DETAIL
- GS_INSTANCE_TIME
- GS_LABELS
- GS_LSC_MEMORY_DETAIL
- GS_MASKING
- GS_MATVIEWS
- GS_OS_RUN_INFO
- GS_REDO_STAT
- GS_SESSION_CPU_STATISTICS
- GS_SESSION_MEMORY
- GS_SESSION_MEMORY_CONTEXT
- GS_SESSION_MEMORY_DETAIL
- GS_SESSION_MEMORY_STATISTICS
- GS_SESSION_STAT
- GS_SESSION_TIME
- GS_SHARED_MEMORY_DETAIL
- GS_SQL_COUNT
- GS_STAT_SESSION_CU
- GS_THREAD_MEMORY_CONTEXT
- GS_TOTAL_MEMORY_DETAIL
- GS_WLM_CGROUP_INFO
- GS_WLM_EC_OPERATOR_STATISTICS
- GS_WLM_OPERATOR_HISTORY
- GS_WLM_OPERATOR_STATISTICS
- GS_WLM_PLAN_OPERATOR_HISTORY
- GS_WLM_REBUILD_USER_RESOURCE_POOL
- GS_WLM_RESOURCE_POOL
- GS_WLM_SESSION_HISTORY
- GS_WLM_SESSION_INFO
- GS_WLM_SESSION_INFO_ALL
- GS_WLM_SESSION_STATISTICS
- GS_WLM_USER_INFO
- IOS_STATUS
- MPP_TABLES
- PG_AVAILABLE_EXTENSION_VERSIONS
- PG_AVAILABLE_EXTENSIONS
- PG_COMM_DELAY
- PG_COMM_RECV_STREAM
- PG_COMM_SEND_STREAM
- PG_COMM_STATUS
- PG_CONTROL_GROUP_CONFIG
- PG_CURSORS
- PG_EXT_STATS
- PG_GET_INVALID_BACKENDS
- PG_GET_SENDERS_CATCHUP_TIME
- PG_GROUP
- PG_GTT_ATTACHED_PIDS
- PG_GTT_RELSTATS
- PG_GTT_STATS
- PG_INDEXES
- PG_LOCKS
- PG_NODE_ENV
- PG_OS_THREADS
- PG_PREPARED_STATEMENTS
- PG_PREPARED_XACTS
- PG_PUBLICATION_TABLES
- PG_REPLICATION_ORIGIN_STATUS
- PG_REPLICATION_SLOTS
- PG_RLSPOLICIES
- PG_ROLES
- PG_RULES
- PG_RUNNING_XACTS
- PG_SECLABELS
- PG_SESSION_IOSTAT
- PG_SESSION_WLMSTAT
- PG_SETTINGS
- PG_SHADOW
- PG_STAT_ACTIVITY
- PG_STAT_ACTIVITY_NG
- PG_STAT_ALL_INDEXES
- PG_STAT_ALL_TABLES
- PG_STAT_BAD_BLOCK
- PG_STAT_BGWRITER
- PG_STAT_DATABASE
- PG_STAT_DATABASE_CONFLICTS
- PG_STAT_REPLICATION
- PG_STAT_SUBSCRIPTION
- PG_STAT_SYS_INDEXES
- PG_STAT_SYS_TABLES
- PG_STAT_USER_FUNCTIONS
- PG_STAT_USER_INDEXES
- PG_STAT_USER_TABLES
- PG_STAT_XACT_ALL_TABLES
- PG_STAT_XACT_SYS_TABLES
- PG_STAT_XACT_USER_FUNCTIONS
- PG_STAT_XACT_USER_TABLES
- PG_STATIO_ALL_INDEXES
- PG_STATIO_ALL_SEQUENCES
- PG_STATIO_ALL_TABLES
- PG_STATIO_SYS_INDEXES
- PG_STATIO_SYS_SEQUENCES
- PG_STATIO_SYS_TABLES
- PG_STATIO_USER_INDEXES
- PG_STATIO_USER_SEQUENCES
- PG_STATIO_USER_TABLES
- PG_STATS
- PG_TABLES
- PG_TDE_INFO
- PG_THREAD_WAIT_STATUS
- PG_TIMEZONE_ABBREVS
- PG_TIMEZONE_NAMES
- PG_TOTAL_MEMORY_DETAIL
- PG_TOTAL_USER_RESOURCE_INFO
- PG_TOTAL_USER_RESOURCE_INFO_OID
- PG_USER
- PG_USER_MAPPINGS
- PG_VARIABLE_INFO
- PG_VIEWS
- PG_WLM_STATISTICS
- PGXC_PREPARED_XACTS
- PLAN_TABLE
- PATCH_INFORMATION_TABLE
- 系统函数
- 逻辑操作符
- 比较操作符
- 字符处理函数和操作符
- 二进制字符串函数和操作符
- 位串函数和操作符
- 模式匹配操作符
- 数字操作函数和操作符
- 时间和日期处理函数和操作符
- 类型转换函数
- 几何函数和操作符
- 网络地址函数和操作符
- 文本检索函数和操作符
- JSON/JSONB函数和操作符
- HLL函数和操作符
- SEQUENCE函数
- 数组函数和操作符
- 范围函数和操作符
- 聚集函数
- 窗口函数(分析函数)
- 安全函数
- 账本数据库的函数
- 密态等值的函数
- 返回集合的函数
- 条件表达式函数
- 系统信息函数
- 系统管理函数
- 统计信息函数
- 触发器函数
- 事件触发器函数
- HashFunc函数
- 提示信息函数
- 全局临时表函数
- 故障注入系统函数
- AI特性函数
- 动态数据脱敏函数
- 其他系统函数
- 内部函数
- Global SysCache特性函数
- 数据损坏检测修复函数
- XML类型函数
- 废弃函数
- 支持的数据类型
- SQL语法
- ABORT
- ALTER AGGREGATE
- ALTER AUDIT POLICY
- ALTER DATABASE
- ALTER DATA SOURCE
- ALTER DEFAULT PRIVILEGES
- ALTER DIRECTORY
- ALTER EVENT
- ALTER EVENT TRIGGER
- ALTER EXTENSION
- ALTER FOREIGN DATA WRAPPER
- ALTER FOREIGN TABLE
- ALTER FUNCTION
- ALTER GLOBAL CONFIGURATION
- ALTER GROUP
- ALTER INDEX
- ALTER LANGUAGE
- ALTER LARGE OBJECT
- ALTER MASKING POLICY
- ALTER MATERIALIZED VIEW
- ALTER OPERATOR
- ALTER PACKAGE
- ALTER PROCEDURE
- ALTER PUBLICATION
- ALTER RESOURCE LABEL
- ALTER RESOURCE POOL
- ALTER ROLE
- ALTER ROW LEVEL SECURITY POLICY
- ALTER RULE
- ALTER SCHEMA
- ALTER SEQUENCE
- ALTER SERVER
- ALTER SESSION
- ALTER SUBSCRIPTION
- ALTER SYNONYM
- ALTER SYSTEM KILL SESSION
- ALTER SYSTEM SET
- ALTER TABLE
- ALTER TABLE PARTITION
- ALTER TABLE SUBPARTITION
- ALTER TABLESPACE
- ALTER TEXT SEARCH CONFIGURATION
- ALTER TEXT SEARCH DICTIONARY
- ALTER TRIGGER
- ALTER TYPE
- ALTER USER
- ALTER USER MAPPING
- ALTER VIEW
- ANALYZE | ANALYSE
- BEGIN
- CALL
- CHECKPOINT
- CLEAN CONNECTION
- CLOSE
- CLUSTER
- COMMENT
- COMMIT | END
- COMMIT PREPARED
- CONNECT BY
- COPY
- CREATE AGGREGATE
- CREATE AUDIT POLICY
- CREATE CAST
- CREATE CLIENT MASTER KEY
- CREATE COLUMN ENCRYPTION KEY
- CREATE DATABASE
- CREATE DATA SOURCE
- CREATE DIRECTORY
- CREATE EVENT
- CREATE EVENT TRIGGER
- CREATE EXTENSION
- CREATE FOREIGN DATA WRAPPER
- CREATE FOREIGN TABLE
- CREATE FUNCTION
- CREATE GROUP
- CREATE INCREMENTAL MATERIALIZED VIEW
- CREATE INDEX
- CREATE LANGUAGE
- CREATE MASKING POLICY
- CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW
- CREATE MODEL
- CREATE OPERATOR
- CREATE PACKAGE
- CREATE PROCEDURE
- CREATE PUBLICATION
- CREATE RESOURCE LABEL
- CREATE RESOURCE POOL
- CREATE ROLE
- CREATE ROW LEVEL SECURITY POLICY
- CREATE RULE
- CREATE SCHEMA
- CREATE SEQUENCE
- CREATE SERVER
- CREATE SUBSCRIPTION
- CREATE SYNONYM
- CREATE TABLE
- CREATE TABLE AS
- CREATE TABLE PARTITION
- CREATE TABLESPACE
- CREATE TABLE SUBPARTITION
- CREATE TEXT SEARCH CONFIGURATION
- CREATE TEXT SEARCH DICTIONARY
- CREATE TRIGGER
- CREATE TYPE
- CREATE USER
- CREATE USER MAPPING
- CREATE VIEW
- CREATE WEAK PASSWORD DICTIONARY
- CURSOR
- DEALLOCATE
- DECLARE
- DELETE
- DELIMITER
- DO
- DROP AGGREGATE
- DROP AUDIT POLICY
- DROP CAST
- DROP CLIENT MASTER KEY
- DROP COLUMN ENCRYPTION KEY
- DROP DATABASE
- DROP DATA SOURCE
- DROP DIRECTORY
- DROP EVENT
- DROP EVENT TRIGGER
- DROP EXTENSION
- DROP FOREIGN DATA WRAPPER
- DROP FOREIGN TABLE
- DROP FUNCTION
- DROP GLOBAL CONFIGURATION
- DROP GROUP
- DROP INDEX
- DROP LANGUAGE
- DROP MASKING POLICY
- DROP MATERIALIZED VIEW
- DROP MODEL
- DROP OPERATOR
- DROP OWNED
- DROP PACKAGE
- DROP PROCEDURE
- DROP PUBLICATION
- DROP RESOURCE LABEL
- DROP RESOURCE POOL
- DROP ROLE
- DROP ROW LEVEL SECURITY POLICY
- DROP RULE
- DROP SCHEMA
- DROP SEQUENCE
- DROP SERVER
- DROP SUBSCRIPTION
- DROP SYNONYM
- DROP TABLE
- DROP TABLESPACE
- DROP TEXT SEARCH CONFIGURATION
- DROP TEXT SEARCH DICTIONARY
- DROP TRIGGER
- DROP TYPE
- DROP USER
- DROP USER MAPPING
- DROP VIEW
- DROP WEAK PASSWORD DICTIONARY
- EXECUTE
- EXECUTE DIRECT
- EXPLAIN
- EXPLAIN PLAN
- FETCH
- GRANT
- INSERT
- LOCK
- MERGE INTO
- MOVE
- PREDICT BY
- PREPARE
- PREPARE TRANSACTION
- PURGE
- REASSIGN OWNED
- REFRESH INCREMENTAL MATERIALIZED VIEW
- REFRESH MATERIALIZED VIEW
- REINDEX
- RELEASE SAVEPOINT
- RESET
- REVOKE
- ROLLBACK
- ROLLBACK PREPARED
- ROLLBACK TO SAVEPOINT
- SAVEPOINT
- SELECT
- SELECT INTO
- SET
- SET CONSTRAINTS
- SET ROLE
- SET SESSION AUTHORIZATION
- SET TRANSACTION
- SHOW
- SHOW EVENTS
- SHRINK
- SHUTDOWN
- SNAPSHOT
- START TRANSACTION
- TIMECAPSULE TABLE
- TRUNCATE
- UPDATE
- VACUUM
- VALUES
- SQL参考
- GUC参数说明
- Schema
- Information Schema
- DBE_PERF
- OS
- Instance
- Memory
- File
- Object
- STAT_USER_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STAT_USER_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STAT_USER_TABLES
- STAT_USER_INDEXES
- SUMMARY_STAT_USER_INDEXES
- GLOBAL_STAT_USER_INDEXES
- STAT_SYS_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STAT_SYS_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STAT_SYS_TABLES
- STAT_SYS_INDEXES
- SUMMARY_STAT_SYS_INDEXES
- GLOBAL_STAT_SYS_INDEXES
- STAT_ALL_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STAT_ALL_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STAT_ALL_TABLES
- STAT_ALL_INDEXES
- SUMMARY_STAT_ALL_INDEXES
- GLOBAL_STAT_ALL_INDEXES
- STAT_DATABASE
- SUMMARY_STAT_DATABASE
- GLOBAL_STAT_DATABASE
- STAT_DATABASE_CONFLICTS
- SUMMARY_STAT_DATABASE_CONFLICTS
- GLOBAL_STAT_DATABASE_CONFLICTS
- STAT_XACT_ALL_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STAT_XACT_ALL_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STAT_XACT_ALL_TABLES
- STAT_XACT_SYS_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STAT_XACT_SYS_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STAT_XACT_SYS_TABLES
- STAT_XACT_USER_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STAT_XACT_USER_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STAT_XACT_USER_TABLES
- STAT_XACT_USER_FUNCTIONS
- SUMMARY_STAT_XACT_USER_FUNCTIONS
- GLOBAL_STAT_XACT_USER_FUNCTIONS
- STAT_BAD_BLOCK
- SUMMARY_STAT_BAD_BLOCK
- GLOBAL_STAT_BAD_BLOCK
- STAT_USER_FUNCTIONS
- SUMMARY_STAT_USER_FUNCTIONS
- GLOBAL_STAT_USER_FUNCTIONS
- Workload
- Session/Thread
- SESSION_STAT
- GLOBAL_SESSION_STAT
- SESSION_TIME
- GLOBAL_SESSION_TIME
- SESSION_MEMORY
- GLOBAL_SESSION_MEMORY
- SESSION_MEMORY_DETAIL
- GLOBAL_SESSION_MEMORY_DETAIL
- SESSION_STAT_ACTIVITY
- GLOBAL_SESSION_STAT_ACTIVITY
- THREAD_WAIT_STATUS
- GLOBAL_THREAD_WAIT_STATUS
- LOCAL_THREADPOOL_STATUS
- GLOBAL_THREADPOOL_STATUS
- SESSION_CPU_RUNTIME
- SESSION_MEMORY_RUNTIME
- STATEMENT_IOSTAT_COMPLEX_RUNTIME
- LOCAL_ACTIVE_SESSION
- Transaction
- Query
- STATEMENT
- SUMMARY_STATEMENT
- STATEMENT_COUNT
- GLOBAL_STATEMENT_COUNT
- SUMMARY_STATEMENT_COUNT
- GLOBAL_STATEMENT_COMPLEX_HISTORY
- GLOBAL_STATEMENT_COMPLEX_HISTORY_TABLE
- GLOBAL_STATEMENT_COMPLEX_RUNTIME
- STATEMENT_RESPONSETIME_PERCENTILE
- STATEMENT_COMPLEX_RUNTIME
- STATEMENT_COMPLEX_HISTORY_TABLE
- STATEMENT_COMPLEX_HISTORY
- STATEMENT_WLMSTAT_COMPLEX_RUNTIME
- STATEMENT_HISTORY
- Cache/IO
- STATIO_USER_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_USER_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_USER_TABLES
- STATIO_USER_INDEXES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_USER_INDEXES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_USER_INDEXES
- STATIO_USER_SEQUENCES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_USER_SEQUENCES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_USER_SEQUENCES
- STATIO_SYS_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_SYS_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_SYS_TABLES
- STATIO_SYS_INDEXES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_SYS_INDEXES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_SYS_INDEXES
- STATIO_SYS_SEQUENCES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_SYS_SEQUENCES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_SYS_SEQUENCES
- STATIO_ALL_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_ALL_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_ALL_TABLES
- STATIO_ALL_INDEXES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_ALL_INDEXES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_ALL_INDEXES
- STATIO_ALL_SEQUENCES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_ALL_SEQUENCES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_ALL_SEQUENCES
- GLOBAL_STAT_DB_CU
- GLOBAL_STAT_SESSION_CU
- Utility
- REPLICATION_STAT
- GLOBAL_REPLICATION_STAT
- REPLICATION_SLOTS
- GLOBAL_REPLICATION_SLOTS
- BGWRITER_STAT
- GLOBAL_BGWRITER_STAT
- GLOBAL_CKPT_STATUS
- GLOBAL_DOUBLE_WRITE_STATUS
- GLOBAL_PAGEWRITER_STATUS
- GLOBAL_RECORD_RESET_TIME
- GLOBAL_REDO_STATUS
- GLOBAL_RECOVERY_STATUS
- CLASS_VITAL_INFO
- USER_LOGIN
- SUMMARY_USER_LOGIN
- GLOBAL_GET_BGWRITER_STATUS
- GLOBAL_SINGLE_FLUSH_DW_STATUS
- GLOBAL_CANDIDATE_STATUS
- Lock
- Wait Events
- Configuration
- Operator
- Workload Manager
- Global Plancache
- RTO
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER Schema
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.turn_on
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.turn_off
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.local_debug_server_info
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.attach
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.info_locals
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.next
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.continue
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.abort
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.print_var
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.info_code
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.step
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.add_breakpoint
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.delete_breakpoint
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.info_breakpoints
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.backtrace
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.disable_breakpoint
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.enable_breakpoint
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.finish
- DBE_PLDEBUGGER.set_var
- DB4AI Schema
- DBE_PLDEVELOPER
- DBE_SQL_UTIL Schema
- 工具参考
- 工具一览表
- 客户端工具
- 服务端工具
- 系统内部使用的工具
- dsscmd
- dssserver
- mogdb
- gs_backup
- gs_basebackup
- gs_ctl
- gs_initdb
- gs_install
- gs_postuninstall
- gs_preinstall
- gs_sshexkey
- gs_tar
- gs_uninstall
- gs_upgradectl
- gs_expansion
- gs_dropnode
- gs_probackup
- gstrace
- kdb5_util
- kadmin.local
- kinit
- klist
- krb5kdc
- kdestroy
- pg_config
- pg_controldata
- pg_recvlogical
- pg_resetxlog
- pg_archivecleanup
- pssh
- pscp
- transfer.py
- FAQ
- MogDB可运行脚本功能说明
- gs_collector工具支持收集的系统表和视图列表
- 数据库报错信息
- SQL标准错误码说明
- 第三方库错误码说明
- GAUSS-00001 - GAUSS-00100
- GAUSS-00101 - GAUSS-00200
- GAUSS 00201 - GAUSS 00300
- GAUSS 00301 - GAUSS 00400
- GAUSS 00401 - GAUSS 00500
- GAUSS 00501 - GAUSS 00600
- GAUSS 00601 - GAUSS 00700
- GAUSS 00701 - GAUSS 00800
- GAUSS 00801 - GAUSS 00900
- GAUSS 00901 - GAUSS 01000
- GAUSS 01001 - GAUSS 01100
- GAUSS 01101 - GAUSS 01200
- GAUSS 01201 - GAUSS 01300
- GAUSS 01301 - GAUSS 01400
- GAUSS 01401 - GAUSS 01500
- GAUSS 01501 - GAUSS 01600
- GAUSS 01601 - GAUSS 01700
- GAUSS 01701 - GAUSS 01800
- GAUSS 01801 - GAUSS 01900
- GAUSS 01901 - GAUSS 02000
- GAUSS 02001 - GAUSS 02100
- GAUSS 02101 - GAUSS 02200
- GAUSS 02201 - GAUSS 02300
- GAUSS 02301 - GAUSS 02400
- GAUSS 02401 - GAUSS 02500
- GAUSS 02501 - GAUSS 02600
- GAUSS 02601 - GAUSS 02700
- GAUSS 02701 - GAUSS 02800
- GAUSS 02801 - GAUSS 02900
- GAUSS 02901 - GAUSS 03000
- GAUSS 03001 - GAUSS 03100
- GAUSS 03101 - GAUSS 03200
- GAUSS 03201 - GAUSS 03300
- GAUSS 03301 - GAUSS 03400
- GAUSS 03401 - GAUSS 03500
- GAUSS 03501 - GAUSS 03600
- GAUSS 03601 - GAUSS 03700
- GAUSS 03701 - GAUSS 03800
- GAUSS 03801 - GAUSS 03900
- GAUSS 03901 - GAUSS 04000
- GAUSS 04001 - GAUSS 04100
- GAUSS 04101 - GAUSS 04200
- GAUSS 04201 - GAUSS 04300
- GAUSS 04301 - GAUSS 04400
- GAUSS 04401 - GAUSS 04500
- GAUSS 04501 - GAUSS 04600
- GAUSS 04601 - GAUSS 04700
- GAUSS 04701 - GAUSS 04800
- GAUSS 04801 - GAUSS 04900
- GAUSS 04901 - GAUSS 05000
- GAUSS 05001 - GAUSS 05100
- GAUSS 05101 - GAUSS 05200
- GAUSS 05201 - GAUSS 05300
- GAUSS 05301 - GAUSS 05400
- GAUSS 05401 - GAUSS 05500
- GAUSS 05501 - GAUSS 05600
- GAUSS 05601 - GAUSS 05700
- GAUSS 05701 - GAUSS 05800
- GAUSS 05801 - GAUSS 05900
- GAUSS 05901 - GAUSS 06000
- GAUSS 06001 - GAUSS 06100
- GAUSS 06101 - GAUSS 06200
- GAUSS 06201 - GAUSS 06300
- GAUSS 06301 - GAUSS 06400
- GAUSS 06401 - GAUSS 06500
- GAUSS 06501 - GAUSS 06600
- GAUSS 06601 - GAUSS 06700
- GAUSS 06701 - GAUSS 06800
- GAUSS 06801 - GAUSS 06900
- GAUSS 06901 - GAUSS 07000
- GAUSS 07001 - GAUSS 07100
- GAUSS 07101 - GAUSS 07200
- GAUSS 07201 - GAUSS 07300
- GAUSS 07301 - GAUSS 07400
- GAUSS 07401 - GAUSS 07500
- GAUSS 50000 - GAUSS 50999
- GAUSS 51000 - GAUSS 51999
- GAUSS 52000 - GAUSS 52999
- GAUSS 53000 - GAUSS 53699
- 错误日志信息参考
- 系统表及系统视图
- 故障诊断指南
- 源码解析
- 常见问题解答 (FAQs)
- 术语表
- 通信矩阵
- Mogeaver
典型SQL调优
SQL调优是一个不断分析与尝试的过程: 试跑Query,判断性能是否满足要求;如果不满足要求,则通过查看执行计划分析原因并进行针对性优化;然后重新试跑和优化,直到满足性能目标。
SQL自诊断
用户在执行查询或者执行INSERT/DELETE/UPDATE/CREATE TABLE AS语句时,可能会遇到性能问题。这种情况下,通过查询GS_WLM_SESSION_STATISTICS,GS_WLM_SESSION_HISTORY视图的warning字段可以获得对应查询可能导致性能问题的告警信息,为性能调优提供参考。
SQL自诊断的告警类型与resource_track_level的设置有关系。如果resource_track_level设置为query,则可以诊断多列/单列统计信息未收集和SQL不下推的告警。如果resource_track_level设置为operator,则可以诊断所有的告警场景。
SQL自诊断的诊断范围与resource_track_cost的设置有关系。当SQL的代价大于resource_track_cost时,SQL才会被诊断。SQL的代价可以通过explain来确认。
告警场景
目前支持对多列/单列统计信息未收集导致性能问题的场景上报告警。
如果存在单列或者多列统计信息未收集,则上报相关告警。调优方法可以参考更新统计信息和统计信息调优。
告警信息示例:
整表的统计信息未收集:
Statistic Not Collect:
schema_test.t1单列统计信息未收集:
Statistic Not Collect:
schema_test.t2(c1,c2)多列统计信息未收集:
Statistic Not Collect:
schema_test.t3((c1,c2))单列和多列统计信息未收集:
Statistic Not Collect:
schema_test.t4(c1,c2) schema_test.t4((c1,c2))规格约束
-
告警字符串长度上限为2048。如果告警信息超过这个长度(例如存在大量未收集统计信息的超长表名,列名等信息)则不告警,只上报warning:
WARNING, "Planner issue report is truncated, the rest of planner issues will be skipped" -
如果query存在limit节点(即查询语句中包含limit),则不会上报limit节点以下的Operator级别的告警。
子查询调优
应用程序通过SQL语句来操作数据库时会使用大量的子查询,这种写法比直接对两个表做连接操作在结构上和思路上更清晰,尤其是在一些比较复杂的查询语句中,子查询有更完整、更独立的语义,会使SQL对业务逻辑的表达更清晰更容易理解,因此得到了广泛的应用。
MogDB根据子查询在SQL语句中的位置把子查询分成了子查询、子链接两种形式。
-
子查询SubQuery: 对应于查询解析树中的范围表RangeTblEntry,更通俗一些指的是出现在FROM语句后面的独立的SELECT语句。
-
子链接SubLink: 对应于查询解析树中的表达式,更通俗一些指的是出现在where/on子句、targetlist里面的语句。
综上,对于查询解析树而言,SubQuery的本质是范围表、而SubLink的本质是表达式。针对SubLink场景而言,由于SubLink可以出现在约束条件、表达式中,按照MogDB对sublink的实现,sublink可以分为以下几类:
-
exist_sublink: 对应EXIST、NOT EXIST语句
-
any_sublink: 对应op ALL(select…)语句,其中OP可以是IN,<,>,=操作符
-
all_sublink: 对应op ALL(select…)语句,其中OP可以是IN,<,>,=操作符
-
rowcompare_sublink: 对应record op (select …)语句
-
expr_sublink: 对应(SELECT with single targetlist item …)语句
-
array_sublink: 对应ARRAY(select…)语句
-
cte_sublink: 对应with query(…)语句
其中OLAP、HTAP场景中常用的sublink为exist_sublink、any_sublink,在MogDB的优化引擎中对其应用场景做了优化(子链接提升),由于SQL语句中子查询的使用的灵活性,会带来SQL子查询过于复杂造成性能问题。子查询从大类上来看,分为非相关子查询和相关子查询:
-
非相关子查询None-Correlated SubQuery
子查询的执行不依赖于外层父查询的任何属性值。这样子查询具有独立性,可独自求解,形成一个子查询计划先于外层的查询求解。
例如:
select t1.c1,t1.c2 from t1 where t1.c1 in ( select c2 from t2 where t2.c2 IN (2,3,4) ); QUERY PLAN ---------------------------------------------------------------- Hash Join Hash Cond: (t1.c1 = t2.c2) -> Seq Scan on t1 Filter: (c1 = ANY ('{2,3,4}'::integer[])) -> Hash -> HashAggregate Group By Key: t2.c2 -> Seq Scan on t2 Filter: (c2 = ANY ('{2,3,4}'::integer[])) (9 rows) -
相关子查询Correlated-SubQuery
子查询的执行依赖于外层父查询的一些属性值(如下列示例t2.c1 = t1.c1条件中的t1.c1)作为内层查询的一个AND-ed条件。这样的子查询不具备独立性,需要和外层查询按分组进行求解。
例如:
select t1.c1,t1.c2 from t1 where t1.c1 in ( select c2 from t2 where t2.c1 = t1.c1 AND t2.c2 in (2,3,4) ); QUERY PLAN ------------------------------------------------------------------------ Seq Scan on t1 Filter: (SubPlan 1) SubPlan 1 -> Seq Scan on t2 Filter: ((c1 = t1.c1) AND (c2 = ANY ('{2,3,4}'::integer[]))) (5 rows)
-
MogDB对SubLink的优化
针对SubLink的优化策略主要是让内层的子查询提升(pullup),能够和外表直接做关联查询,从而避免生成SubPlan+Broadcast內表的执行计划。判断子查询是否存在性能风险,可以通过explain查询语句查看Sublink的部分是否被转换成SubPlan的执行计划。
例如:
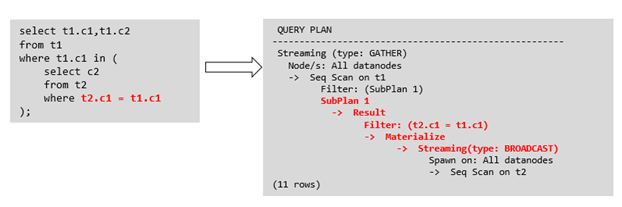
箭头右侧执行计划应替换成下面的执行计划:
QUERY PLAN
--------------------------------
Seq Scan on t1
Filter: (SubPlan 1)
SubPlan 1
-> Seq Scan on t2
Filter: (c1 = t1.c1)
(5 rows)-
目前MogDB支持的Sublink-Release场景
-
IN-Sublink无相关条件
-
不能包含上一层查询的表中的列(可以包含更高层查询表中的列)。
-
不能包含易变函数。
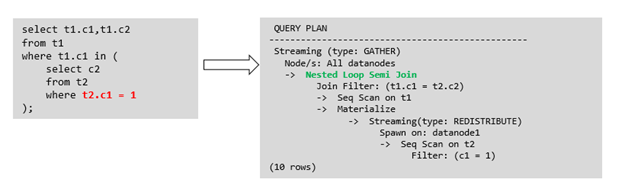
箭头右侧执行计划应替换成下面的执行计划:
QUERY PLAN -------------------------------------- Hash Join Hash Cond: (t1.c1 = t2.c2) -> Seq Scan on t1 -> Hash -> HashAggregate Group By Key: t2.c2 -> Seq Scan on t2 Filter: (c1 = 1) (8 rows)
-
-
Exist-Sublink包含相关条件 Where子句中必须包含上一层查询的表中的列,子查询的其它部分不能含有上层查询的表中的列。其它限制如下。
-
子查询必须有from子句。
-
子查询不能含有with子句。
-
子查询不能含有聚集函数。
-
子查询里不能包含集合操作、排序、limit、windowagg、having操作。
-
不能包含易变函数。
-
不能包含易变函数。
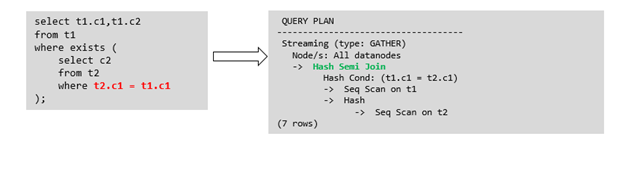
箭头右侧执行计划应替换成下面的执行计划:
QUERY PLAN -------------------------------- Hash Join Hash Cond: (t1.c1 = t2.c1) -> Seq Scan on t1 -> Hash -> HashAggregate Group By Key: t2.c1 -> Seq Scan on t2 (7 rows)
-
-
包含聚集函数的等值相关子查询的提升
子查询的where条件中必须含有来自上一层的列,而且此列必须和子查询本层涉及表中的列做相等判断,且这些条件必须用and连接。其它地方不能包含上层的列。其它限制条件如下。
-
子查询中where条件包含的表达式(列名)必须是表中的列。
-
子查询的Select关键字后,必须有且仅有一个输出列,此输出列必须是聚集函数(如max),并且聚集函数的参数(t2.c2)不能是来自外层表(t1)中的列。聚集函数不能是count。
例如,下列示例可以提升。
select * from t1 where c1 >( select max(t2.c1) from t2 where t2.c1=t1.c1 );下列示例不能提升,因为子查询没有聚集函数。
select * from t1 where c1 >( select t2.c1 from t2 where t2.c1=t1.c1 );下列示例不能提升,因为子查询有两个输出列。
select * from t1 where (c1,c2) >( select max(t2.c1),min(t2.c2) from t2 where t2.c1=t1.c1 ); -
子查询必须是from子句。
-
子查询中不能有groupby、having、集合操作。
-
子查询的targetlist中不能包含返回set的函数。
-
子查询的where条件中必须含有来自上一层的列,而且此列必须和子查询层涉及表中的列做相等判断,且这些条件必须用and连接。其它地方不能包含上层的上层中的列。例如: 下列示例中的最内层子链接可以提升。
select * from t3 where t3.c1=( select t1.c1 from t1 where c1 >( select max(t2.c1) from t2 where t2.c1=t1.c1 ));基于上面的示例,再加一个条件,则不能提升,因为最内侧子查询引用了上层中的列。示例如下:
select * from t3 where t3.c1=( select t1.c1 from t1 where c1 >( select max(t2.c1) from t2 where t2.c1=t1.c1 and t3.c1>t2.c2 ));
-
-
提升OR子句中的SubLink
当WHERE过滤条件中有OR连接的EXIST相关SubLink,
例如:
select a, c from t1 where t1.a = (select avg(a) from t3 where t1.b = t3.b) or exists (select * from t4 where t1.c = t4.c);将OR-ed连接的EXIST相关子查询OR字句的提升过程:
-
提取where条件中,or子句中的opExpr。为: t1.a = (select avg(a) from t3 where t1.b = t3.b)
-
这个op操作中包含subquery,判断是否可以提升,如果可以提升,重写subquery为: select avg(a), t3.b from t3 group by t3.b,生成not null条件t3.b is not null,并将这个opexpr用这个not null条件替换。此时SQL变为:
select a, c from t1 left join (select avg(a) avg, t3.b from t3 group by t3.b) as t3 on (t1.a = avg and t1.b = t3.b) where t3.b is not null or exists (select * from t4 where t1.c = t4.c); -
再次提取or子句中的exists sublink,exists (select * from t4 where t1.c = t4.c),判断是否可以提升,如果可以提升,转换subquery为: select t4.c from t4 group by t4.c生成NotNull条件t4.c is not null提升查询,SQL变为:
select a, c from t1 left join (select avg(a) avg, t3.b from t3 group by t3.b) as t3 on (t1.a = avg and t1.b = t3.b) left join (select t4.c from t4 group by t4.c) where t3.b is not null or t4.c is not null;
-
-
-
目前MogDB不支持的Sublink-Release场景
除了以上场景之外都不支持Sublink提升,因此关联子查询会被计划成SubPlan+Broadcast的执行计划,当inner表的数据量较大时则会产生性能风险。
如果相关子查询中跟外层的两张表做join,那么无法提升该子查询,需要通过将父SQL创建成with子句,然后再跟子查询中的表做相关子查询查询。
例如:
select distinct t1.a, t2.a from t1 left join t2 on t1.a=t2.a and not exists (select a,b from test1 where test1.a=t1.a and test1.b=t2.a);改写为
with temp as ( select * from (select t1.a as a, t2.a as b from t1 left join t2 on t1.a=t2.a) ) select distinct a,b from temp where not exists (select a,b from test1 where temp.a=test1.a and temp.b=test1.b);-
出现在targetlist里的相关子查询无法提升(不含count)
例如:
explain (costs off) select (select c2 from t2 where t1.c1 = t2.c1) ssq, t1.c2 from t1 where t1.c2 > 10;执行计划为:
explain (costs off) select (select c2 from t2 where t1.c1 = t2.c1) ssq, t1.c2 from t1 where t1.c2 > 10; QUERY PLAN -------------------------------- Seq Scan on t1 Filter: (c2 > 10) SubPlan 1 -> Seq Scan on t2 Filter: (t1.c1 = c1) (5 rows)由于相关子查询出现在targetlist(查询返回列表)里,对于t1.c1=t2.c1不匹配的场景仍然需要输出值,因此使用left-outerjoin关联T1&T2确保t1.c1=t2.c1在不匹配时,子SSQ能够返回不匹配的补空值。
 说明:
SSQ和CSSQ的解释如下:
说明:
SSQ和CSSQ的解释如下:- SSQ: ScalarSubQuery一般指返回1行1列scalar值的sublink,简称SSQ。
- CSSQ: Correlated-ScalarSubQuery和SSQ相同不过是指包含相关条件的SSQ。
上述SQL语句可以改写为:
with ssq as ( select t2.c2 from t2 ) select ssq.c2, t1.c2 from t1 left join ssq on t1.c1 = ssq.c2 where t1.c2 > 10;改写后的执行计划为:
QUERY PLAN --------------------------------- Hash Right Join Hash Cond: (ssq.c2 = t1.c1) CTE ssq -> Seq Scan on t2 -> CTE Scan on ssq -> Hash -> Seq Scan on t1 Filter: (c2 > 10) (8 rows)可以看到出现在SSQ返回列表里的相关子查询SSQ,已经被提升成Right Join,从而避免当內表T2较大时出现SubPlan计划导致性能变差。
-
出现在targetlist里的相关子查询无法提升(带count)
例如:
select (select count(*) from t2 where t2.c1=t1.c1) cnt, t1.c1, t3.c1 from t1,t3 where t1.c1=t3.c1 order by cnt, t1.c1;执行计划为
QUERY PLAN -------------------------------------------- Sort Sort Key: ((SubPlan 1)), t1.c1 -> Hash Join Hash Cond: (t1.c1 = t3.c1) -> Seq Scan on t1 -> Hash -> Seq Scan on t3 SubPlan 1 -> Aggregate -> Seq Scan on t2 Filter: (c1 = t1.c1) (11 rows)由于相关子查询出现在targetlist(查询返回列表)里,对于t1.c1=t2.c1不匹配的场景仍然需要输出值,因此使用left-outerjoin关联T1&T2确保t1.c1=t2.c1在不匹配时子SSQ能够返回不匹配的补空值,但是这里带了count语句及时在t1.c1=t2.t1不匹配时需要输出0,因此可以使用一个case-when NULL then 0 else count(*)来代替。
上述SQL语句可以改写为:
with ssq as ( select count(*) cnt, c1 from t2 group by c1 ) select case when ssq.cnt is null then 0 else ssq.cnt end cnt, t1.c1, t3.c1 from t1 left join ssq on ssq.c1 = t1.c1,t3 where t1.c1 = t3.c1 order by ssq.cnt, t1.c1;改写后的执行计划为
QUERY PLAN ------------------------------------------- Sort Sort Key: ssq.cnt, t1.c1 CTE ssq -> HashAggregate Group By Key: t2.c1 -> Seq Scan on t2 -> Hash Join Hash Cond: (t1.c1 = t3.c1) -> Hash Left Join Hash Cond: (t1.c1 = ssq.c1) -> Seq Scan on t1 -> Hash -> CTE Scan on ssq -> Hash -> Seq Scan on t3 (15 rows) -
相关条件为不等值场景
例如:
select t1.c1, t1.c2 from t1 where t1.c1 = (select agg() from t2.c2 > t1.c2);对于非等值相关条件的SubLink目前无法提升,从语义上可以通过做2次join(一次CorrelationKey,一次rownum自关联)达到提升改写的目的。
改写方案有两种。
-
子查询改写方式
select t1.c1, t1.c2 from t1, ( select t1.rowid, agg() aggref from t1,t2 where t1.c2 > t2.c2 group by t1.rowid ) dt /* derived table */ where t1.rowid = dt.rowid AND t1.c1 = dt.aggref; -
CTE改写方式
WITH dt as ( select t1.rowid, agg() aggref from t1,t2 where t1.c2 > t2.c2 group by t1.rowid ) select t1.c1, t1.c2 from t1, derived_table where t1.rowid = derived_table.rowid AND t1.c1 = derived_table.aggref;
须知:
- 对于AGG类型为count(*)时需要进行CASE-WHEN对没有match的场景补0处理,非COUNT(*)场景NULL处理。
- CTE改写方式如果有sharescan支持性能上能够更优。
-
-
更多优化示例
示例:修改select语句,将子查询修改为和主表的join,或者修改为可以提升的subquery,但是在修改前后需要保证语义的正确性。
explain (costs off) select * from t1 where t1.c1 in (select t2.c1 from t2 where t1.c1 = t2.c2);
QUERY PLAN
--------------------------------
Seq Scan on t1
Filter: (SubPlan 1)
SubPlan 1
-> Seq Scan on t2
Filter: (t1.c1 = c2)
(5 rows)上面事例计划中存在一个subPlan,为了消除这个subPlan可以修改语句为:
explain (costs off) select * from t1 where exists (select t2.c1 from t2 where t1.c1 = t2.c2 and t1.c1 = t2.c1);
QUERY PLAN
------------------------------------------
Hash Join
Hash Cond: (t1.c1 = t2.c2)
-> Seq Scan on t1
-> Hash
-> HashAggregate
Group By Key: t2.c2, t2.c1
-> Seq Scan on t2
Filter: (c2 = c1)
(8 rows)从计划可以看出,subPlan消除了,计划变成了两个表的hash join,这样会大大提高执行效率。
统计信息调优
MogDB是基于代价估算生成的最优执行计划。优化器需要根据analyze收集的统计信息行数估算和代价估算,因此统计信息对优化器行数估算和代价估算起着至关重要的作用。通过analyze收集全局统计信息,主要包括: pg_class表中的relpages和reltuples;pg_statistic表中的stadistinct、stanullfrac、stanumbersN、stavaluesN、histogram_bounds等。
实例分析1: 未收集统计信息导致查询性能差
在很多场景下,由于查询中涉及到的表或列没有收集统计信息,会对查询性能有很大的影响。
表结构如下所示:
CREATE TABLE LINEITEM
(
L_ORDERKEY BIGINT NOT NULL
, L_PARTKEY BIGINT NOT NULL
, L_SUPPKEY BIGINT NOT NULL
, L_LINENUMBER BIGINT NOT NULL
, L_QUANTITY DECIMAL(15,2) NOT NULL
, L_EXTENDEDPRICE DECIMAL(15,2) NOT NULL
, L_DISCOUNT DECIMAL(15,2) NOT NULL
, L_TAX DECIMAL(15,2) NOT NULL
, L_RETURNFLAG CHAR(1) NOT NULL
, L_LINESTATUS CHAR(1) NOT NULL
, L_SHIPDATE DATE NOT NULL
, L_COMMITDATE DATE NOT NULL
, L_RECEIPTDATE DATE NOT NULL
, L_SHIPINSTRUCT CHAR(25) NOT NULL
, L_SHIPMODE CHAR(10) NOT NULL
, L_COMMENT VARCHAR(44) NOT NULL
) with (orientation = column, COMPRESSION = MIDDLE);
CREATE TABLE ORDERS
(
O_ORDERKEY BIGINT NOT NULL
, O_CUSTKEY BIGINT NOT NULL
, O_ORDERSTATUS CHAR(1) NOT NULL
, O_TOTALPRICE DECIMAL(15,2) NOT NULL
, O_ORDERDATE DATE NOT NULL
, O_ORDERPRIORITY CHAR(15) NOT NULL
, O_CLERK CHAR(15) NOT NULL
, O_SHIPPRIORITY BIGINT NOT NULL
, O_COMMENT VARCHAR(79) NOT NULL
)with (orientation = column, COMPRESSION = MIDDLE);查询语句如下所示:
explain verbose select
count(*) as numwait
from
lineitem l1,
orders
where
o_orderkey = l1.l_orderkey
and o_orderstatus = 'F'
and l1.l_receiptdate > l1.l_commitdate
and not exists (
select
*
from
lineitem l3
where
l3.l_orderkey = l1.l_orderkey
and l3.l_suppkey <> l1.l_suppkey
and l3.l_receiptdate > l3.l_commitdate
)
order by
numwait desc;当出现该问题时,可以通过如下方法确认查询中涉及到的表或列有没有做过analyze收集统计信息。
-
通过explain verbose执行query分析执行计划时会提示WARNING信息,如下所示:
WARNING:Statistics in some tables or columns(public.lineitem.l_receiptdate, public.lineitem.l_commitdate, public.lineitem.l_orderkey, public.lineitem.l_suppkey, public.orders.o_orderstatus, public.orders.o_orderkey) are not collected. HINT:Do analyze for them in order to generate optimized plan. -
可以通过在pg_log目录下的日志文件中查找以下信息来确认是当前执行的query是否由于没有收集统计信息导致查询性能变差。
2017-06-14 17:28:30.336 CST 140644024579856 20971684 [BACKEND] LOG:Statistics in some tables or columns(public.lineitem.l_receiptdate, public.lineitem.l_commitdate, public.lineitem.l_orderkey, public.linei tem.l_suppkey, public.orders.o_orderstatus, public.orders.o_orderkey) are not collected. 2017-06-14 17:28:30.336 CST 140644024579856 20971684 [BACKEND] HINT:Do analyze for them in order to generate optimized plan.
当通过以上方法查看到哪些表或列没有做analyze,可以通过对WARNING或日志中上报的表或列做analyze可以解决由于为收集统计信息导致查询变慢的问题。
算子级调优
一个查询语句要经过多个算子步骤才会输出最终的结果。由于个别算子耗时过长导致整体查询性能下降的情况比较常见。这些算子是整个查询的瓶颈算子。通用的优化手段是EXPLAIN ANALYZE/PERFORMANCE命令查看执行过程的瓶颈算子,然后进行针对性优化。
如下面的执行过程信息中,Hashagg算子的执行时间占总时间的: (51016-13535)/ 56476 ≈66%,此处Hashagg算子就是这个查询的瓶颈算子,在进行性能优化时应当优先考虑此算子的优化。
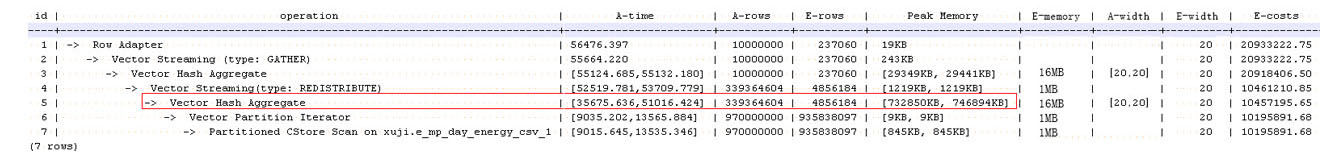
算子级调优示例
示例1:基表扫描时,对于点查或者范围扫描等过滤大量数据的查询,如果使用SeqScan全表扫描会比较耗时,可以在条件列上建立索引选择IndexScan进行索引扫描提升扫描效率。
postgres=# explain (analyze on, costs off) select * from store_sales where ss_sold_date_sk = 2450944;
id | operation | A-time | A-rows | Peak Memory | A-width
----+--------------------------------+---------------------+--------+--------------+---------
1 | -> Streaming (type: GATHER) | 3666.020 | 3360 | 195KB |
2 | -> Seq Scan on store_sales | [3594.611,3594.611] | 3360 | [34KB, 34KB] |
(2 rows)
Predicate Information (identified by plan id)
-----------------------------------------------
2 --Seq Scan on store_sales
Filter: (ss_sold_date_sk = 2450944)
Rows Removed by Filter: 4968936
postgres=# create index idx on store_sales_row(ss_sold_date_sk);
CREATE INDEX
postgres=# explain (analyze on, costs off) select * from store_sales_row where ss_sold_date_sk = 2450944;
id | operation | A-time | A-rows | Peak Memory | A-width
----+------------------------------------------------+-----------------+--------+--------------+----------
1 | -> Streaming (type: GATHER) | 81.524 | 3360 | 195KB |
2 | -> Index Scan using idx on store_sales_row | [13.352,13.352] | 3360 | [34KB, 34KB] |
(2 rows)上述例子中,全表扫描返回3360条数据,过滤掉大量数据,在ss_sold_date_sk列上建立索引后,使用IndexScan扫描效率显著提高,从3.6秒提升到13毫秒。
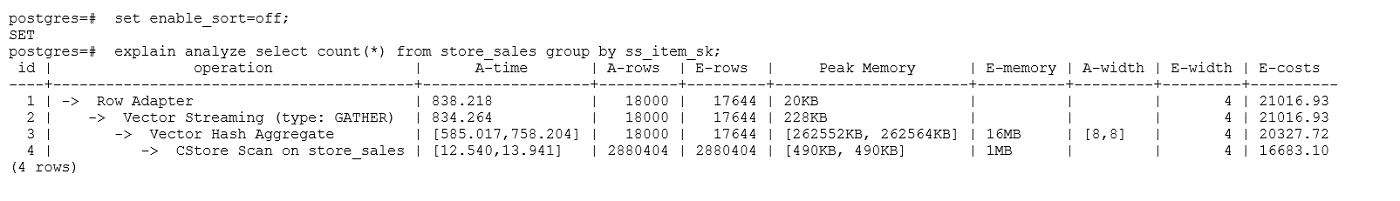
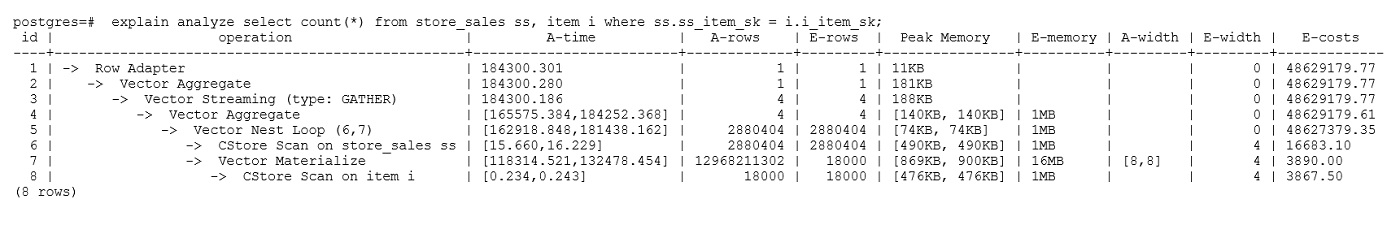
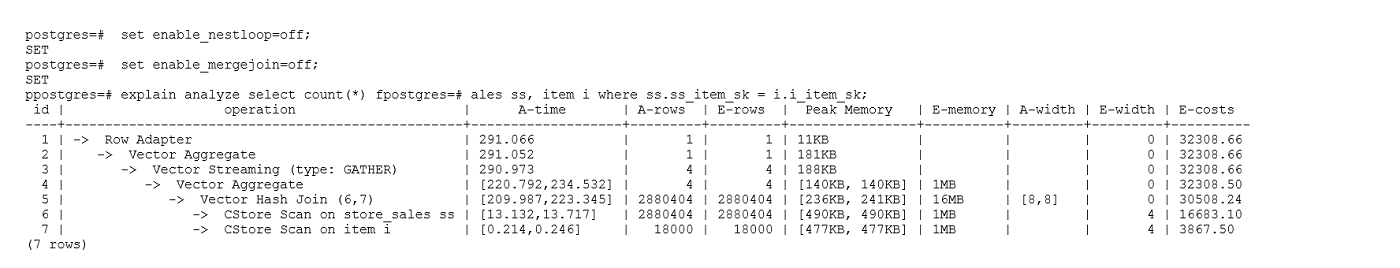
示例2:如果从执行计划中看,两表join选择了NestLoop,而实际行数比较大时,NestLoop Join可能执行比较慢。如下的例子中NestLoop耗时181秒,如果设置参数enable_mergejoin=off关掉Merge Join,同时设置参数enable_nestloop=off关掉NestLoop,让优化器选择HashJoin,则Join耗时提升至200多毫秒。
示例3:通常情况下Agg选择HashAgg性能较好,如果大结果集选择了Sort+GroupAgg,则需要设置enable_sort=off,HashAgg耗时明显优于Sort+GroupAgg。