- About MogDB
- MogDB Introduction
- Comparison Between MogDB and openGauss
- MogDB Release Notes
- High Availability and Performance
- Open Source Components
- Usage Limitations
- Terms of Use
- Quick Start
- Installation Guide
- Container Installation
- Simplified Installation Process
- Standard Installation
- Manual Installation
- Administrator Guide
- Routine Maintenance
- Starting and Stopping MogDB
- Using the gsql Client for Connection
- Routine Maintenance
- Checking OS Parameters
- Checking MogDB Health Status
- Checking Database Performance
- Checking and Deleting Logs
- Checking Time Consistency
- Checking The Number of Application Connections
- Routinely Maintaining Tables
- Routinely Recreating an Index
- Data Security Maintenance Suggestions
- Log Reference
- Primary and Standby Management
- MOT Engine
- Introducing MOT
- Using MOT
- Concepts of MOT
- Appendix
- Column-store Tables Management
- Backup and Restoration
- Importing and Exporting Data
- Importing Data
- Exporting Data
- Upgrade Guide
- Common Fault Locating Cases
- Core Fault Locating
- When the TPC-C is running and a disk to be injected is full, the TPC-C stops responding
- Standby Node in the Need Repair (WAL) State
- Insufficient Memory
- Service Startup Failure
- "Error:No space left on device" Is Displayed
- After You Run the du Command to Query Data File Size In the XFS File System, the Query Result Is Greater than the Actual File Size
- File Is Damaged in the XFS File System
- Primary Node Is Hung in Demoting During a Switchover
- Disk Space Usage Reaches the Threshold and the Database Becomes Read-only
- Slow Response to a Query Statement
- Analyzing the Status of a Query Statement
- Forcibly Terminating a Session
- Analyzing Whether a Query Statement Is Blocked
- Low Query Efficiency
- "Lock wait timeout" Is Displayed When a User Executes an SQL Statement
- Table Size Does not Change After VACUUM FULL Is Executed on the Table
- An Error Is Reported When the Table Partition Is Modified
- Different Data Is Displayed for the Same Table Queried By Multiple Users
- When a User Specifies Only an Index Name to Modify the Index, A Message Indicating That the Index Does Not Exist Is Displayed
- Reindexing Fails
- An Error Occurs During Integer Conversion
- "too many clients already" Is Reported or Threads Failed To Be Created in High Concurrency Scenarios
- B-tree Index Faults
- Routine Maintenance
- Security Guide
- Database Security Management
- Performance Tuning
- System Optimization
- SQL Optimization
- WDR Snapshot Schema
- TPCC Performance Tuning Guide
- Developer Guide
- Application Development Guide
- Development Specifications
- Development Based on JDBC
- Overview
- JDBC Package, Driver Class, and Environment Class
- Development Process
- Loading the Driver
- Connecting to a Database
- Connecting to the Database (Using SSL)
- Running SQL Statements
- Processing Data in a Result Set
- Closing a Connection
- Example: Common Operations
- Example: Retrying SQL Queries for Applications
- Example: Importing and Exporting Data Through Local Files
- Example 2: Migrating Data from a MY Database to MogDB
- Example: Logic Replication Code
- JDBC API Reference
- java.sql.Connection
- java.sql.CallableStatement
- java.sql.DatabaseMetaData
- java.sql.Driver
- java.sql.PreparedStatement
- java.sql.ResultSet
- java.sql.ResultSetMetaData
- java.sql.Statement
- javax.sql.ConnectionPoolDataSource
- javax.sql.DataSource
- javax.sql.PooledConnection
- javax.naming.Context
- javax.naming.spi.InitialContextFactory
- CopyManager
- Development Based on ODBC
- Development Based on libpq
- Development Based on libpq
- libpq API Reference
- Database Connection Control Functions
- Database Statement Execution Functions
- Functions for Asynchronous Command Processing
- Functions for Canceling Queries in Progress
- Example
- Connection Characters
- Commissioning
- Appendices
- Stored Procedure
- User Defined Functions
- Autonomous Transaction
- Logical Replication
- Logical Decoding
- Foreign Data Wrapper
- Materialized View
- Materialized View Overview
- Full Materialized View
- Incremental Materialized View
- AI Features
- Overview
- Predictor: AI Query Time Forecasting
- X-Tuner: Parameter Optimization and Diagnosis
- SQLdiag: Slow SQL Discovery
- A-Detection: Status Monitoring
- Index-advisor: Index Recommendation
- DeepSQL
- Application Development Guide
- Reference Guide
- System Catalogs and System Views
- Overview of System Catalogs and System Views
- System Catalogs
- GS_AUDITING_POLICY
- GS_AUDITING_POLICY_ACCESS
- GS_AUDITING_POLICY_FILTERS
- GS_AUDITING_POLICY_PRIVILEGES
- GS_CLIENT_GLOBAL_KEYS
- GS_CLIENT_GLOBAL_KEYS_ARGS
- GS_COLUMN_KEYS
- GS_COLUMN_KEYS_ARGS
- GS_ENCRYPTED_COLUMNS
- GS_MASKING_POLICY
- GS_MASKING_POLICY_ACTIONS
- GS_MASKING_POLICY_FILTERS
- GS_MATVIEW
- GS_MATVIEW_DEPENDENCY
- GS_OPT_MODEL
- GS_POLICY_LABEL
- GS_WLM_INSTANCE_HISTORY
- GS_WLM_OPERATOR_INFO
- GS_WLM_PLAN_ENCODING_TABLE
- GS_WLM_PLAN_OPERATOR_INFO
- GS_WLM_USER_RESOURCE_HISTORY
- PG_AGGREGATE
- PG_AM
- PG_AMOP
- PG_AMPROC
- PG_APP_WORKLOADGROUP_MAPPING
- PG_ATTRDEF
- PG_ATTRIBUTE
- PG_AUTHID
- PG_AUTH_HISTORY
- PG_AUTH_MEMBERS
- PG_CAST
- PG_CLASS
- PG_COLLATION
- PG_CONSTRAINT
- PG_CONVERSION
- PG_DATABASE
- PG_DB_ROLE_SETTING
- PG_DEFAULT_ACL
- PG_DEPEND
- PG_DESCRIPTION
- PG_DIRECTORY
- PG_ENUM
- PG_EXTENSION
- PG_EXTENSION_DATA_SOURCE
- PG_FOREIGN_DATA_WRAPPER
- PG_FOREIGN_SERVER
- PG_FOREIGN_TABLE
- PG_INDEX
- PG_INHERITS
- PG_JOB
- PG_JOB_PROC
- PG_LANGUAGE
- PG_LARGEOBJECT
- PG_LARGEOBJECT_METADATA
- PG_NAMESPACE
- PG_OBJECT
- PG_OPCLASS
- PG_OPERATOR
- PG_OPFAMILY
- PG_PARTITION
- PG_PLTEMPLATE
- PG_PROC
- PG_RANGE
- PG_RESOURCE_POOL
- PG_REWRITE
- PG_RLSPOLICY
- PG_SECLABEL
- PG_SHDEPEND
- PG_SHDESCRIPTION
- PG_SHSECLABEL
- PG_STATISTIC
- PG_STATISTIC_EXT
- PG_SYNONYM
- PG_TABLESPACE
- PG_TRIGGER
- PG_TS_CONFIG
- PG_TS_CONFIG_MAP
- PG_TS_DICT
- PG_TS_PARSER
- PG_TS_TEMPLATE
- PG_TYPE
- PG_USER_MAPPING
- PG_USER_STATUS
- PG_WORKLOAD_GROUP
- PLAN_TABLE_DATA
- STATEMENT_HISTORY
- System Views
- GS_AUDITING
- GS_AUDITING_ACCESS
- GS_AUDITING_PRIVILEGE
- GS_CLUSTER_RESOURCE_INFO
- GS_INSTANCE_TIME
- GS_LABELS
- GS_MASKING
- GS_MATVIEWS
- GS_SESSION_MEMORY
- GS_SESSION_CPU_STATISTICS
- GS_SESSION_MEMORY_CONTEXT
- GS_SESSION_MEMORY_DETAIL
- GS_SESSION_MEMORY_STATISTICS
- GS_SQL_COUNT
- GS_WLM_CGROUP_INFO
- GS_WLM_PLAN_OPERATOR_HISTORY
- GS_WLM_REBUILD_USER_RESOURCE_POOL
- GS_WLM_RESOURCE_POOL
- GS_WLM_USER_INFO
- GS_STAT_SESSION_CU
- GS_TOTAL_MEMORY_DETAIL
- MPP_TABLES
- PG_AVAILABLE_EXTENSION_VERSIONS
- PG_AVAILABLE_EXTENSIONS
- PG_COMM_DELAY
- PG_COMM_RECV_STREAM
- PG_COMM_SEND_STREAM
- PG_COMM_STATUS
- PG_CONTROL_GROUP_CONFIG
- PG_CURSORS
- PG_EXT_STATS
- PG_GET_INVALID_BACKENDS
- PG_GET_SENDERS_CATCHUP_TIME
- PG_GROUP
- PG_GTT_RELSTATS
- PG_GTT_STATS
- PG_GTT_ATTACHED_PIDS
- PG_INDEXES
- PG_LOCKS
- PG_NODE_ENV
- PG_OS_THREADS
- PG_PREPARED_STATEMENTS
- PG_PREPARED_XACTS
- PG_REPLICATION_SLOTS
- PG_RLSPOLICIES
- PG_ROLES
- PG_RULES
- PG_SECLABELS
- PG_SETTINGS
- PG_SHADOW
- PG_STATS
- PG_STAT_ACTIVITY
- PG_STAT_ALL_INDEXES
- PG_STAT_ALL_TABLES
- PG_STAT_BAD_BLOCK
- PG_STAT_BGWRITER
- PG_STAT_DATABASE
- PG_STAT_DATABASE_CONFLICTS
- PG_STAT_USER_FUNCTIONS
- PG_STAT_USER_INDEXES
- PG_STAT_USER_TABLES
- PG_STAT_REPLICATION
- PG_STAT_SYS_INDEXES
- PG_STAT_SYS_TABLES
- PG_STAT_XACT_ALL_TABLES
- PG_STAT_XACT_SYS_TABLES
- PG_STAT_XACT_USER_FUNCTIONS
- PG_STAT_XACT_USER_TABLES
- PG_STATIO_ALL_INDEXES
- PG_STATIO_ALL_SEQUENCES
- PG_STATIO_ALL_TABLES
- PG_STATIO_SYS_INDEXES
- PG_STATIO_SYS_SEQUENCES
- PG_STATIO_SYS_TABLES
- PG_STATIO_USER_INDEXES
- PG_STATIO_USER_SEQUENCES
- PG_STATIO_USER_TABLES
- PG_TABLES
- PG_TDE_INFO
- PG_THREAD_WAIT_STATUS
- PG_TIMEZONE_ABBREVS
- PG_TIMEZONE_NAMES
- PG_TOTAL_MEMORY_DETAIL
- PG_TOTAL_USER_RESOURCE_INFO
- PG_TOTAL_USER_RESOURCE_INFO_OID
- PG_USER
- PG_USER_MAPPINGS
- PG_VARIABLE_INFO
- PG_VIEWS
- PLAN_TABLE
- GS_FILE_STAT
- GS_OS_RUN_INFO
- GS_REDO_STAT
- GS_SESSION_STAT
- GS_SESSION_TIME
- GS_THREAD_MEMORY_CONTEXT
- Functions and Operators
- Logical Operators
- Comparison Operators
- Character Processing Functions and Operators
- Binary String Functions and Operators
- Bit String Functions and Operators
- Mode Matching Operators
- Mathematical Functions and Operators
- Date and Time Processing Functions and Operators
- Type Conversion Functions
- Geometric Functions and Operators
- Network Address Functions and Operators
- Text Search Functions and Operators
- JSON Functions
- HLL Functions and Operators
- SEQUENCE Functions
- Array Functions and Operators
- Range Functions and Operators
- Aggregate Functions
- Window Functions
- Security Functions
- Encrypted Equality Functions
- Set Returning Functions
- Conditional Expression Functions
- System Information Functions
- System Administration Functions
- Statistics Information Functions
- Trigger Functions
- Global Temporary Table Functions
- AI Feature Functions
- Other System Functions
- Internal Functions
- Obsolete Functions
- Supported Data Types
- SQL Syntax
- ABORT
- ALTER AGGREGATE
- ALTER AUDIT POLICY
- ALTER DATABASE
- ALTER DATA SOURCE
- ALTER DEFAULT PRIVILEGES
- ALTER DIRECTORY
- ALTER EXTENSION
- ALTER FOREIGN TABLE
- ALTER FUNCTION
- ALTER GROUP
- ALTER INDEX
- ALTER LANGUAGE
- ALTER LARGE OBJECT
- ALTER MASKING POLICY
- ALTER MATERIALIZED VIEW
- ALTER OPERATOR
- ALTER RESOURCE LABEL
- ALTER ROLE
- ALTER ROW LEVEL SECURITY POLICY
- ALTER RULE
- ALTER SCHEMA
- ALTER SEQUENCE
- ALTER SERVER
- ALTER SESSION
- ALTER SYNONYM
- ALTER SYSTEM KILL SESSION
- ALTER SYSTEM SET
- ALTER TABLE
- ALTER TABLE PARTITION
- ALTER TABLESPACE
- ALTER TEXT SEARCH CONFIGURATION
- ALTER TEXT SEARCH DICTIONARY
- ALTER TRIGGER
- ALTER TYPE
- ALTER USER
- ALTER USER MAPPING
- ALTER VIEW
- ANALYZE | ANALYSE
- BEGIN
- CALL
- CHECKPOINT
- CLOSE
- CLUSTER
- COMMENT
- COMMIT | END
- COMMIT PREPARED
- COPY
- CREATE AGGREGATE
- CREATE AUDIT POLICY
- CREATE CAST
- CREATE CLIENT MASTER KEY
- CREATE COLUMN ENCRYPTION KEY
- CREATE DATABASE
- CREATE DATA SOURCE
- CREATE DIRECTORY
- CREATE EXTENSION
- CREATE FOREIGN TABLE
- CREATE FUNCTION
- CREATE GROUP
- CREATE INCREMENTAL MATERIALIZED VIEW
- CREATE INDEX
- CREATE LANGUAGE
- CREATE MASKING POLICY
- CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW
- CREATE OPERATOR
- CREATE ROW LEVEL SECURITY POLICY
- CREATE PROCEDURE
- CREATE RESOURCE LABEL
- CREATE ROLE
- CREATE RULE
- CREATE SCHEMA
- CREATE SEQUENCE
- CREATE SERVER
- CREATE SYNONYM
- CREATE TABLE
- CREATE TABLE AS
- CREATE TABLE PARTITION
- CREATE TABLESPACE
- CREATE TEXT SEARCH CONFIGURATION
- CREATE TEXT SEARCH DICTIONARY
- CREATE TRIGGER
- CREATE TYPE
- CREATE USER
- CREATE USER MAPPING
- CREATE VIEW
- CURSOR
- DEALLOCATE
- DECLARE
- DELETE
- DO
- DROP AGGREGATE
- DROP AUDIT POLICY
- DROP CAST
- DROP CLIENT MASTER KEY
- DROP COLUMN ENCRYPTION KEY
- DROP DATABASE
- DROP DATA SOURCE
- DROP DIRECTORY
- DROP EXTENSION
- DROP FOREIGN TABLE
- DROP FUNCTION
- DROP GROUP
- DROP INDEX
- DROP LANGUAGE
- DROP MASKING POLICY
- DROP MATERIALIZED VIEW
- DROP OPERATOR
- DROP OWNED
- DROP RESOURCE LABEL
- DROP ROW LEVEL SECURITY POLICY
- DROP PROCEDURE
- DROP ROLE
- DROP RULE
- DROP SCHEMA
- DROP SEQUENCE
- DROP SERVER
- DROP SYNONYM
- DROP TABLE
- DROP TABLESPACE
- DROP TEXT SEARCH CONFIGURATION
- DROP TEXT SEARCH DICTIONARY
- DROP TRIGGER
- DROP TYPE
- DROP USER
- DROP USER MAPPING
- DROP VIEW
- EXECUTE
- EXPLAIN
- EXPLAIN PLAN
- FETCH
- GRANT
- INSERT
- LOCK
- MOVE
- MERGE INTO
- PREPARE
- PREPARE TRANSACTION
- REASSIGN OWNED
- REFRESH INCREMENTAL MATERIALIZED VIEW
- REFRESH MATERIALIZED VIEW
- REINDEX
- RELEASE SAVEPOINT
- RESET
- REVOKE
- ROLLBACK
- ROLLBACK PREPARED
- ROLLBACK TO SAVEPOINT
- SAVEPOINT
- SELECT
- SELECT INTO
- SET
- SET CONSTRAINTS
- SET ROLE
- SET SESSION AUTHORIZATION
- SET TRANSACTION
- SHOW
- SHUTDOWN
- START TRANSACTION
- TRUNCATE
- UPDATE
- VACUUM
- VALUES
- SQL Reference
- MogDB SQL
- Keywords
- Constant and Macro
- Expressions
- Type Conversion
- Full Text Search
- Introduction
- Tables and Indexes
- Controlling Text Search
- Additional Features
- Parser
- Dictionaries
- Configuration Examples
- Testing and Debugging Text Search
- Limitations
- System Operation
- Controlling Transactions
- DDL Syntax Overview
- DML Syntax Overview
- DCL Syntax Overview
- Appendix
- GUC Parameters
- GUC Parameter Usage
- File Location
- Connection and Authentication
- Resource Consumption
- Parallel Import
- Write Ahead Log
- HA Replication
- Memory Table
- Query Planning
- Error Reporting and Logging
- Alarm Detection
- Statistics During the Database Running
- Load Management
- Automatic Vacuuming
- Default Settings of Client Connection
- Lock Management
- Version and Platform Compatibility
- Faut Tolerance
- Connection Pool Parameters
- MogDB Transaction
- Developer Options
- Auditing
- Upgrade Parameters
- Miscellaneous Parameters
- Wait Events
- Query
- System Performance Snapshot
- Equality Query in a Fully-encrypted Database
- Global Temporary Table
- Scheduled Task
- Thread Pool
- Appendix
- Information Schema
- DBE_PERF
- DBE_PERF Overview
- OS
- Instance
- Memory
- File
- Object
- STAT_USER_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STAT_USER_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STAT_USER_TABLES
- STAT_USER_INDEXES
- SUMMARY_STAT_USER_INDEXES
- GLOBAL_STAT_USER_INDEXES
- STAT_SYS_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STAT_SYS_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STAT_SYS_TABLES
- STAT_SYS_INDEXES
- SUMMARY_STAT_SYS_INDEXES
- GLOBAL_STAT_SYS_INDEXES
- STAT_ALL_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STAT_ALL_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STAT_ALL_TABLES
- STAT_ALL_INDEXES
- SUMMARY_STAT_ALL_INDEXES
- GLOBAL_STAT_ALL_INDEXES
- STAT_DATABASE
- SUMMARY_STAT_DATABASE
- GLOBAL_STAT_DATABASE
- STAT_DATABASE_CONFLICTS
- SUMMARY_STAT_DATABASE_CONFLICTS
- GLOBAL_STAT_DATABASE_CONFLICTS
- STAT_XACT_ALL_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STAT_XACT_ALL_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STAT_XACT_ALL_TABLES
- STAT_XACT_SYS_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STAT_XACT_SYS_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STAT_XACT_SYS_TABLES
- STAT_XACT_USER_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STAT_XACT_USER_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STAT_XACT_USER_TABLES
- STAT_XACT_USER_FUNCTIONS
- SUMMARY_STAT_XACT_USER_FUNCTIONS
- GLOBAL_STAT_XACT_USER_FUNCTIONS
- STAT_BAD_BLOCK
- SUMMARY_STAT_BAD_BLOCK
- GLOBAL_STAT_BAD_BLOCK
- STAT_USER_FUNCTIONS
- SUMMARY_STAT_USER_FUNCTIONS
- GLOBAL_STAT_USER_FUNCTIONS
- Workload
- Session/Thread
- SESSION_STAT
- GLOBAL_SESSION_STAT
- SESSION_TIME
- GLOBAL_SESSION_TIME
- SESSION_MEMORY
- GLOBAL_SESSION_MEMORY
- SESSION_MEMORY_DETAIL
- GLOBAL_SESSION_MEMORY_DETAIL
- SESSION_STAT_ACTIVITY
- GLOBAL_SESSION_STAT_ACTIVITY
- THREAD_WAIT_STATUS
- GLOBAL_THREAD_WAIT_STATUS
- LOCAL_THREADPOOL_STATUS
- GLOBAL_THREADPOOL_STATUS
- SESSION_CPU_RUNTIME
- SESSION_MEMORY_RUNTIME
- STATEMENT_IOSTAT_COMPLEX_RUNTIME
- Transaction
- Query
- STATEMENT
- SUMMARY_STATEMENT
- STATEMENT_COUNT
- GLOBAL_STATEMENT_COUNT
- SUMMARY_STATEMENT_COUNT
- GLOBAL_STATEMENT_COMPLEX_HISTORY
- GLOBAL_STATEMENT_COMPLEX_HISTORY_TABLE
- GLOBAL_STATEMENT_COMPLEX_RUNTIME
- STATEMENT_RESPONSETIME_PERCENTILE
- STATEMENT_USER_COMPLEX_HISTORY
- STATEMENT_COMPLEX_RUNTIME
- STATEMENT_COMPLEX_HISTORY_TABLE
- STATEMENT_COMPLEX_HISTORY
- STATEMENT_WLMSTAT_COMPLEX_RUNTIME
- STATEMENT_HISTORY
- Cache/IO
- STATIO_USER_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_USER_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_USER_TABLES
- STATIO_USER_INDEXES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_USER_INDEXES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_USER_INDEXES
- STATIO_USER_SEQUENCES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_USER_SEQUENCES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_USER_SEQUENCES
- STATIO_SYS_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_SYS_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_SYS_TABLES
- STATIO_SYS_INDEXES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_SYS_INDEXES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_SYS_INDEXES
- STATIO_SYS_SEQUENCES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_SYS_SEQUENCES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_SYS_SEQUENCES
- STATIO_ALL_TABLES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_ALL_TABLES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_ALL_TABLES
- STATIO_ALL_INDEXES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_ALL_INDEXES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_ALL_INDEXES
- STATIO_ALL_SEQUENCES
- SUMMARY_STATIO_ALL_SEQUENCES
- GLOBAL_STATIO_ALL_SEQUENCES
- GLOBAL_STAT_DB_CU
- GLOBAL_STAT_SESSION_CU
- Utility
- REPLICATION_STAT
- GLOBAL_REPLICATION_STAT
- REPLICATION_SLOTS
- GLOBAL_REPLICATION_SLOTS
- BGWRITER_STAT
- GLOBAL_BGWRITER_STAT
- GLOBAL_CKPT_STATUS
- GLOBAL_DOUBLE_WRITE_STATUS
- GLOBAL_PAGEWRITER_STATUS
- GLOBAL_RECORD_RESET_TIME
- GLOBAL_REDO_STATUS
- GLOBAL_RECOVERY_STATUS
- CLASS_VITAL_INFO
- USER_LOGIN
- SUMMARY_USER_LOGIN
- GLOBAL_GET_BGWRITER_STATUS
- Lock
- Wait Events
- Configuration
- Operator
- Workload Manager
- Global Plancache
- Appendix
- Tool Reference
- Tool Overview
- Client Tool
- Server Tools
- Tools Used in the Internal System
- Error Code Reference
- Description of SQL Error Codes
- Third-Party Library Error Codes
- GAUSS-00001 - GAUSS-00100
- GAUSS-00101 - GAUSS-00200
- GAUSS 00201 - GAUSS 00300
- GAUSS 00301 - GAUSS 00400
- GAUSS 00401 - GAUSS 00500
- GAUSS 00501 - GAUSS 00600
- GAUSS 00601 - GAUSS 00700
- GAUSS 00701 - GAUSS 00800
- GAUSS 00801 - GAUSS 00900
- GAUSS 00901 - GAUSS 01000
- GAUSS 01001 - GAUSS 01100
- GAUSS 01101 - GAUSS 01200
- GAUSS 01201 - GAUSS 01300
- GAUSS 01301 - GAUSS 01400
- GAUSS 01401 - GAUSS 01500
- GAUSS 01501 - GAUSS 01600
- GAUSS 01601 - GAUSS 01700
- GAUSS 01701 - GAUSS 01800
- GAUSS 01801 - GAUSS 01900
- GAUSS 01901 - GAUSS 02000
- GAUSS 02001 - GAUSS 02100
- GAUSS 02101 - GAUSS 02200
- GAUSS 02201 - GAUSS 02300
- GAUSS 02301 - GAUSS 02400
- GAUSS 02401 - GAUSS 02500
- GAUSS 02501 - GAUSS 02600
- GAUSS 02601 - GAUSS 02700
- GAUSS 02701 - GAUSS 02800
- GAUSS 02801 - GAUSS 02900
- GAUSS 02901 - GAUSS 03000
- GAUSS 03001 - GAUSS 03100
- GAUSS 03101 - GAUSS 03200
- GAUSS 03201 - GAUSS 03300
- GAUSS 03301 - GAUSS 03400
- GAUSS 03401 - GAUSS 03500
- GAUSS 03501 - GAUSS 03600
- GAUSS 03601 - GAUSS 03700
- GAUSS 03701 - GAUSS 03800
- GAUSS 03801 - GAUSS 03900
- GAUSS 03901 - GAUSS 04000
- GAUSS 04001 - GAUSS 04100
- GAUSS 04101 - GAUSS 04200
- GAUSS 04201 - GAUSS 04300
- GAUSS 04301 - GAUSS 04400
- GAUSS 04401 - GAUSS 04500
- GAUSS 04501 - GAUSS 04600
- GAUSS 04601 - GAUSS 04700
- GAUSS 04701 - GAUSS 04800
- GAUSS 04801 - GAUSS 04900
- GAUSS 04901 - GAUSS 05000
- GAUSS 05001 - GAUSS 05100
- GAUSS 05101 - GAUSS 05200
- GAUSS 05201 - GAUSS 05300
- GAUSS 05301 - GAUSS 05400
- GAUSS 05401 - GAUSS 05500
- GAUSS 05501 - GAUSS 05600
- GAUSS 05601 - GAUSS 05700
- GAUSS 05701 - GAUSS 05800
- GAUSS 05801 - GAUSS 05900
- GAUSS 05901 - GAUSS 06000
- GAUSS 06001 - GAUSS 06100
- GAUSS 06101 - GAUSS 06200
- GAUSS 06201 - GAUSS 06300
- GAUSS 06301 - GAUSS 06400
- GAUSS 06401 - GAUSS 06500
- GAUSS 06501 - GAUSS 06600
- GAUSS 06601 - GAUSS 06700
- GAUSS 06701 - GAUSS 06800
- GAUSS 06801 - GAUSS 06900
- GAUSS 06901 - GAUSS 07000
- GAUSS 07001 - GAUSS 07100
- GAUSS 07101 - GAUSS 07200
- GAUSS 07201 - GAUSS 07300
- GAUSS 07301 - GAUSS 07400
- GAUSS 07401 - GAUSS 07480
- GAUSS 50000 - GAUSS 50999
- GAUSS 51000 - GAUSS 51999
- GAUSS 52000 - GAUSS 52999
- GAUSS 53000 - GAUSS 53699
- System Catalogs and System Views
- FAQs
- Glossary
Product FAQs
Q1. What is the relationship between ultimate RTO, parallel recovery, and standby node readability?
The configurations of ultimate RTO, parallel recovery, and standby node readability are as follows:
- Ultimate RTO: recovery_parse_workers indicates the number of Xlog threads parsed during parallel recovery. recovery_parallelism indicates the actual number of Xlog threads during parallel recovery. When recovery_parse_workers is greater than 1, ultimate RTO recovery is implemented. Only when both recovery_parse_workers and recovery_parallelism are set to a value greater than 1, can parallel recovery be implemented.
- Parallel recovery: recovery_max_workers specifies the maximum number of threads for parallel recovery. recovery_parallelism specifies the actual number of threads for parallel recovery. If the value of recovery_max_workers is greater than 1, parallel recovery is configured. However, only when recovery_max_workers and recovery_parallelism are set to a value greater than 1, can parallel recovery be implemented.
- Standby node readability: hot_standby indicates that a hot standby node can be read during recovery. If the value of hot_standby is true, the standby node can be read.
Parallel recovery is a file-level parallel redo, and the ultimate RTO is a data block-level parallel recovery. Parallel recovery is compatible with standby node readability, but ultimate RTO is incompatible with standby node readability. During configuration of preceding parameters, code check (with CheckExtremeRtoGUCConflicts) is performed. If recovery_parse_workers is set to a value greater than 1 and hot_standby is set to true, an error will be reported.
Q2. How can I select a candidate primary node for primary/standby switchover when the standby node cannot be read in the ultimate RTO scenario?
The standby node cannot be read only when the RTO is ultimate. In serial recovery and parallel recovery, the standby node can be read. If the ultimate RTO is used, only the synchronous mode can be configured, and a node is selected randomly as the primary. After the synchronous mode is used, the data on all nodes is the same.
Q3. What is the function of the template database? Which tables are contained in the template database?
The template database provides a method of quickly creating a database. When creating a database, you can specify the TEMPLATE parameter to create a database by copying a template database.
The template database does not contain any user table. You can view the attributes of the template database in the PG_DATABASE system catalog.
Q4. When MogDB supports physical replication, does the standby node replay logs by page in parallel mode?
MogDB supports two parallel recovery modes: file-level recovery and page-level recovery.
Q5: Is MogDB a distributed database?
No. MogDB supports only primary/standby deployment in standalone mode currently.
MogDB uses the distributed middleware pgpool-II or Shardingsphere to deal with sharding and non-native distributed requests.
Q6: What are MogDB application scenarios?
MogDB application scenarios are similar to those of postgreSQL. MogDB can be applied to e-commerce, finance, O2O, and telecom CRM/billing which feature high concurrency and large data volume.
Application scenarios include transactional application scenarios which focus on online transaction processing and IoT application scenarios which focus on industrial monitoring, remote control, smart cities, smart homes, and IoV.
MogDB provides not only basic functions of relational databases but enhanced HA and monitoring functions for enterprise application scenarios and features.
Q7: Can MogDB be deployed on x86 servers? What are the recommended hardware configurations?
MogDB can be installed on x86 servers (AMD64 architecture). For details, see Hardware Requirements。
Q8: Can MogDB be deployed on KUNPENG servers? What are the recommended hardware configurations?
MogDB can be deployed on KUNPENG servers (ARM architecture) with the recommended hardware configurations the same as those of x86 servers.
Actually, the performance of MogDB on KUNPENG servers is better than that on x86 servers. Therefore, you are advised to choose domestic chip servers.
Q9: Is MogDB free? How is MogDB charged?
MogDB is not free (openGauss is free). MogDB is designed for enterprise users and is not open to individuals. For details about the pricing rules, please contact the sales personnel for consultation.
Q10: What does the database compatibility setting mean during MogDB database creation? What is done to data types for being compatible with different databases?
During MogDB database creation, you can set the DBCOMPATIBILITY parameter to make MogDB compatible with different databases. However, compatibility here refers to only data storage structure compatibility and does not include SQL syntax compatibility.
Currently, you can configure MogDB compatible with Oracle, MySQL, or PostgreSQL. The default setting is that MogDB is compatible with Oracle.
-
For the compatibility type of Oracle, the database considers an empty string as null and replace the data type DATE with TIMESTAMP(0) WITHOUT TIME ZONE.
-
For the compatibility type of MySQL, when a string is converted to an integer type, if an illegal value is entered, it will be converted to 0. However, for other compatibility types, an error will be reported.
-
For the compatibility type of PostgreSQL, CHAR and VARCHAR use character as the string unit. For other compatibility types, byte is used as the string unit.
For example, as for UTF-8 character set, CHAR(3) can hold 3 Chinese characters in the compatibility type of PG but only one Chinese character in the other compatibility types.
If you need to create a database compatible with PostgreSQL, the syntax format is "CREATE DATABASE dbname DBCOMPATIBILITY='PG';."
Parameter description:
DBCOMPATIBILITY [ = ] compatibility_type
Specifies the type of the database to be compatible with.
Value range: A, B, C, and PG
A indicates that MogDB is compatible with Oracle. B indicates that MogDB is compatible with MySQL. C indicates that MogDB is compatible with Teradata. PG indicates that MogDB is compatible with PostgreSQL. However, C is not supported currently. Therefore, the values A, B, and PG are commonly used.
Q11: What are major improvement of MogDB based on traditional PostgreSQL? What are advantages of MogDB?
For technical implementation:
- most_available_sync (If the synchronous standby node fails, the services of the primary node will not be interrupted.)
- XIDs that cannot be exhausted
- Physical replication slot automatically created in the stream replication environment
- Incremental checkpoints
- Double write
For ecological consideration:
-
Modified based on openGauss and dependent on the Huawei R&D team
-
Completely autonomous and controllable
-
Integrated ecological tools, including PTK, MTK, RWT, MIT, SCA, and BRM
Additionally, part of tools are being developed.
-
Active community and rich materials
Q12: What is the MogDB performance in terms of the Intel processor?
| Test Item | Data Volume | Number of Concurrent Requests | Average CPU Usage | IOPS | IO Delay | Number of WALs | tpmC | Test Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single node | 100 GB | 500 | 29.39% | 6.50K | 1.94 ms | 3974 | 520896.3 | 10 minutes |
| One primary, one synchronous, and one asynchronous nodes | 100 GB | 500 | 30.4% | 5.31K | 453.2 us | 3944 | 519993.5 | 10 minutes |
| One primary and two synchronous nodes | 100 GB | 500 | 26.35% | 7.66K | 531.9 us | 3535 | 480842.2 | 10 minutes |
Q13: Which OSs can MogDB be deployed on? Is there any compatibility problems?
MogDB can be deployed on the following OSs:
- ARM:
- openEuler 20.03LTS (recommended)
- Kylin OS V10
- x86:
- openEuler 20.03LTS
- CentOS 7.6
- Asianux 7.6
Different OSs and CPU architectures have compatibility problems.
Q14: What are distinctions between MogDB and Oracle in implementation of MVCC?
Oracle is based on SCN, stores data in data blocks, uses undo segments in a circular fashion, and supports the flashback function. However, there exists a large number of transaction rollbacks and too old snapshots (ORA-01555). MogDB is based on transaction ID (TXID), supports row-level storage, does not need undo segments, and supports instantaneous rollback of large transactions. However, there exists block page space and performance overhead problems.
Q15: What are advantages of MogDB incremental checkpoints?
Incremental checkpoints can refresh dirty pages in small batches, in stages, or rolling mode, update LSN information, and reclaim unwanted Xlogs, thereby preventing the performance from being affected by the impact on disks caused by fully refreshing dirty pages.
Q16: How does MogDB deal with XID exhaustion occurred in native PostgreSQL?
MogDB changes transaction ID from int32 to int64. 64-bit XIDs cannot be exhausted for ever. Expired XIDs also need to be frozen but the risk of XID rollback failure will never occur.
Q17: What are distinctions between MogDB AND Oracle in user permission?
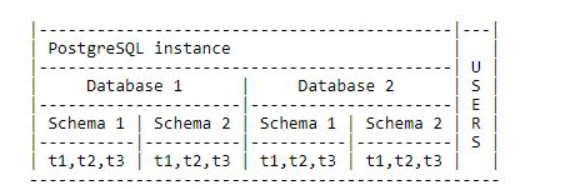
Oracle schema and user are the same concept. But they are not the same in MogDB. In MogDB, all objects created by a user are under a specified schema (or namespace). Other users may have or may not have permission to access these objects or even they cannot create objects in the schema. User (or role) are global objects and not defined in a database but in an instance. Schema is created in a specified database which includes database objects.
Q18: What is the difference between double write in MogDB and second commit in MySQL?
The implementation principle of double write is the same as that of second commit in MySQL. It aims to maintain data consistency and avoid data loss due to damaged data blocks so that data can be recovered.
Q19: What are distinctions between MogDB primary/standby and Oracle Data Guard?
The standby database can receive query requests to share the pressure with the primary database in both MogDB and Oracle.
Q20: Is concurrent physical backup supported? Can physical backup be performed remotely? How can data files be transmitted to the target machine during remote physical backup?
gs_probackup supports concurrent physical backup. Physical backup can be performed remotely to transmit data files to the target machine by using the archive file or stream protocol.
Q21: What is the difference when xlog-method is set to stream or fetch during physical backup?
xlog-method indicates the Xlog transmission mode. If you do not set the parameter, the default value is stream. The stream mode includes all WALs generated during backup. The fetch mode collects WALs at the end of backup. Therefore, the value of wal_keep_segments needs to be set high enough so that logs will not be removed by the end of the backup. If logs have been removed during log transmission, the backup will fail and become unavailable. The stream mode transmits WALs during backup creation, which will start a second connection to a server and transmit WALs during backup. Therefore, the stream mode uses a maximum of two connections determined by the max_wal_senders parameter. The stream mode does not need to store additional WALs only when the client can receive WALs constantly.